TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is the best Computer or Laptop for CAD Software such as Autocad, Solidworks, Inventor, or Revit?
What is CAD-Software anyway, and why is it so difficult to find reliable information on what type of Hardware Components you need to build a high-end PC for CAD?
Well, let’s dive right in!
What is CAD Software and what is it not?
You might have already read some of our other articles that talk about building the best Computer for Digital Content Creation software such as Cinema 4D, After Effects, or for Video Editing and 3D Modeling & Rendering.
The thing is, though, Software such as Cinema 4D, Maya, 3DS Max, or Blender are not CAD Software.
CAD and DCC Software have some fundamental differences, that will also influence what Parts you should pick for your new CAD Workstation.
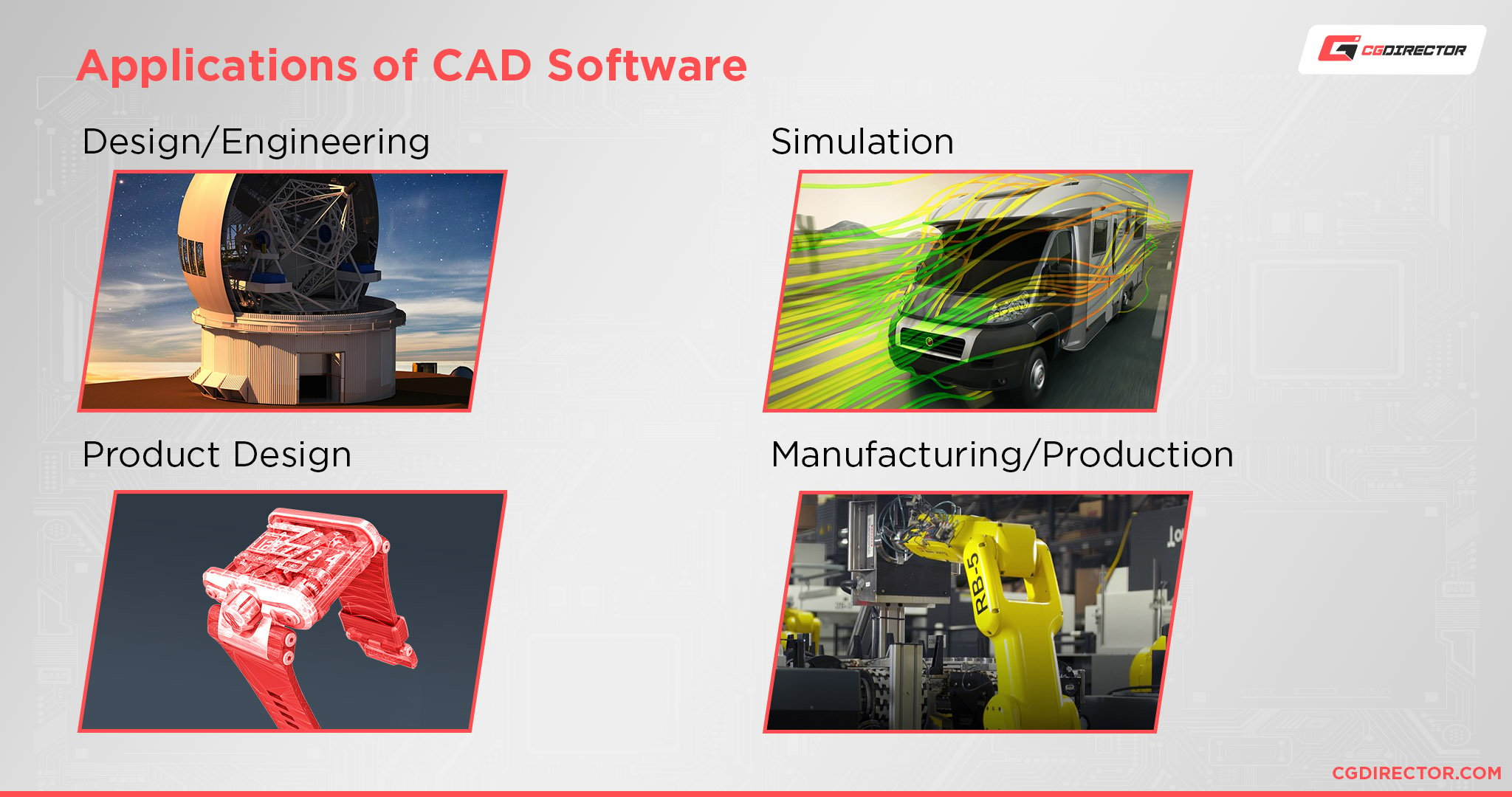
The main difference between these two types of Application-Categories is that DCC Apps are targeted at Content Creation for visual purposes.
They don’t necessarily need high precision but rather should make an Image or Animation look believable or photorealistic, but not mathematically correct.
Because, hey, when I go watch a VFX Movie, that Space ship hovering over the Earth is quite believable, but if it is Mathematically correct and physically possible, is not really the issue here.
Another important factor in DCC Software such as Cinema 4D or Maya is, that they are mainly based on Polygons and not Curves.
If you have enough Polygons you can make an object look round and smooth, even though it is actually made up of many tiny flat faces.
CAD Software though is targeted at mathematically precise forms of object creation that are physically possible. If you zoom in on a car that was modeled in Solidworks, it will always be smooth, no matter how close you zoom in. (Sort of like the difference between Vector Software [CAD] and Pixel-based Software [DCC])
Content that simulates real-life properties.
It is of utmost importance that e.g. a rocket nozzle on a SpaceX Booster Engine is modeled and can be stress-tested and simulated to an extremely high mathematical degree.
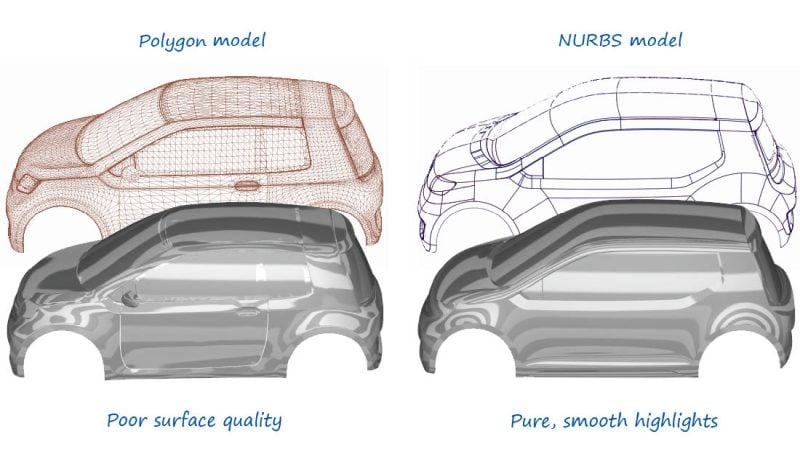
Image-Source: Autodesk
For the sake of this article, I’ll define polygon 3D Software Packages as “DCC” (Cinema 4D, Maya, 3dsmax, Blender, ..) and the Precision Software Packages as “CAD” (Solidworks, Autocad, Revit, Inventor, SolidEdge …).
CAD Software comes in many forms and from many different Brands, some open-source, some proprietary, and expensive.
In this article on building the best Workstation for CAD Workloads, I’ll focus on Autocad, Solidworks, Inventor, and Revit, as these are among the most popular CAD Packages.
Of course, lots of the theory and Part Recommendations can also be applied to other CAD Software as they all tend to work very similarly.
How do CAD Apps utilize the Hardware?
Very Similar to 3D Modeling and Rendering workloads in DCC Apps, CAD Software benefits from a high-clocking CPU – for active work.
Active work means, you are sitting in front of your workstation and actively modeling and working on a project.
These I call attended tasks and they require you to interact and be present at all times, otherwise, your project does not progress.
The other type of task is the unattended task. This includes things like Rendering or Simulation and other processing tasks.
Unattended tasks run on their own and usually take longer than a few milliseconds to process (often hours or days).
Tasks that take days to process have a higher probability to be targeted by developers earlier in order to make them ready for multi-processing.
And of course, as soon as these tasks can be worked on by multiple cores simultaneously, they can be processed much faster.
Look at this Single VS Multi-Core Performance scaling to get a feel for how more Cores can improve performance in workloads that support multi-threading (e.g. Rendering – Cinebench Benchmark):
| CPU Name | Cores | Ghz | Single Score | Multi Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 3 3300X | 4 | 3.8 | 1299 | 6787 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 2600X | 6 | 3.6 | 1094 | 7523 |
| Apple M1 | 8 | 3.2 | 1528 | 7799 |
| Apple M2 | 8 | 3.5 | 1701 | 8538 |
| AMD Threadripper 1900X | 8 | 3.8 | 1005 | 8979 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600 | 6 | 3.6 | 1245 | 9073 |
| Intel Core i7 9700K | 8 | 3.6 | 1285 | 9428 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600X | 6 | 3.8 | 1323 | 9526 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600XT | 6 | 3.8 | 1330 | 9945 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 2700X | 8 | 3.7 | 1102 | 10140 |
For speeding up tasks that can be parallelized (Rendering, (Most) Simulation, Image Processing ..), you will need the maximum number of Cores and not necessarily a high core clock.
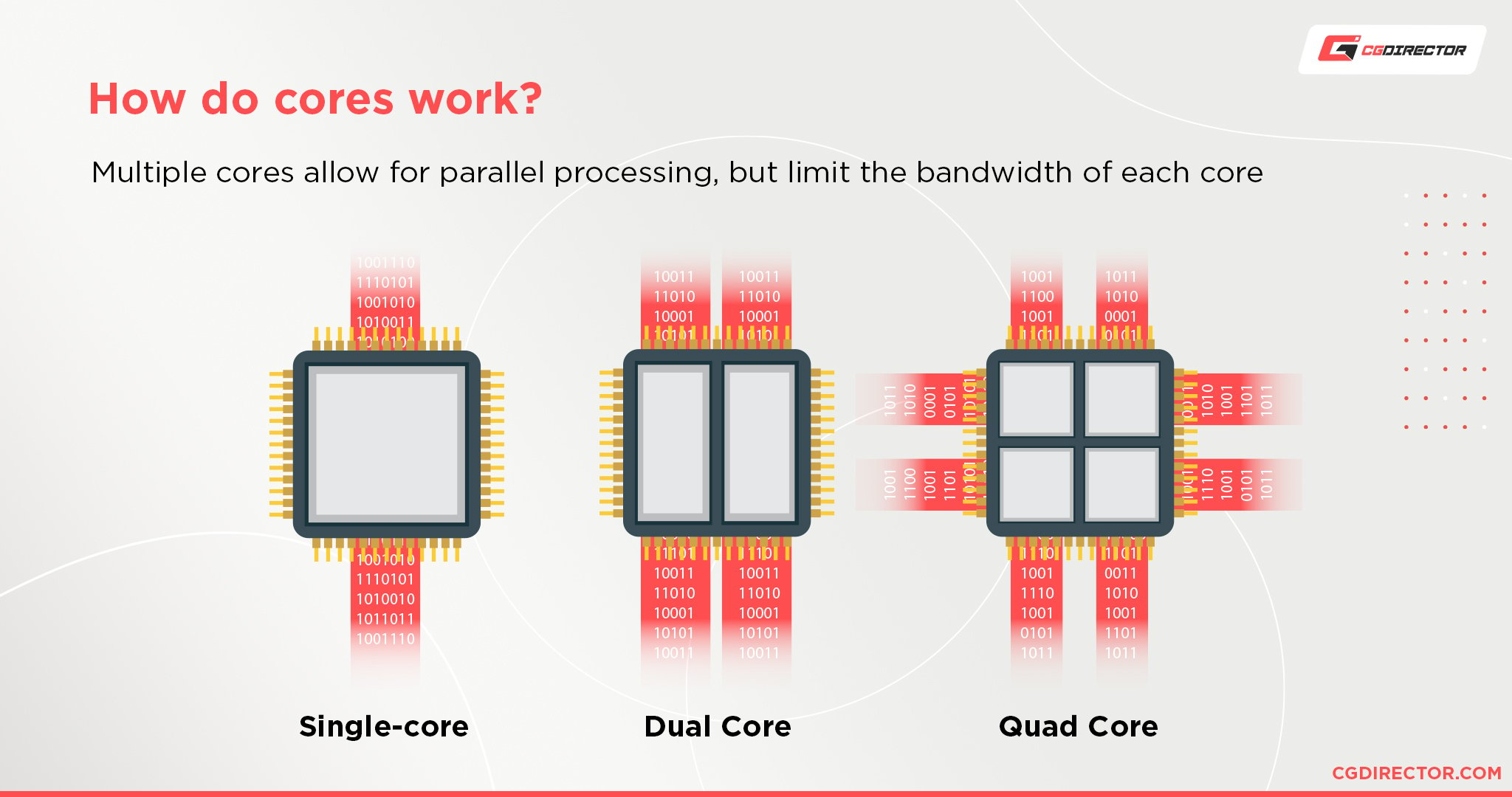
Of course, having both, a high core clock and lots of cores is best, but not always possible.
So to recap:
- Your Active Work performance requires a high-clocking CPU
- Parallelizable tasks such as Rendering and Processing need lots of Cores.
Best Hardware for CAD
So let’s apply this to some real Hardware. What parts do we need for a PC anyway and what components make the CAD work we do the fastest?
Best Processor (CPU) for CAD Software
As you can see in these benchmarks that measure the CPU performance in Solidworks, we find a strong parallel to the Cinebench Benchmark, which lets us easily measure CPU Performance.
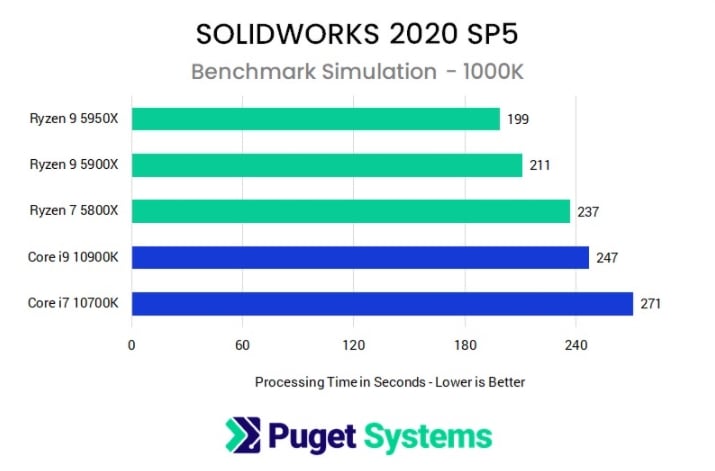
Image-Source: Pugetsystems
Here’s the Cinebench R23 Benchmark in comparison:
▮ = AMD | ▮ = Intel
| CPU Name | Cores | Ghz | Single Score | Multi Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | 8 | 4.6 | 1811 | 17762 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D | 12 | 4.4 | 2039 | 27084 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D | 16 | 4.2 | 2043 | 38581 |
| Intel Core i5 14600K | 14 | 3.5 | 2097 | 24683 |
| Intel Core i7 14700K | 20 | 3.4 | 2228 | 33572 |
| Intel Core i9 13900KS | 24 | 3.2 | 2317 | 40986 |
| Intel Core i9 14900K | 24 | 3.2 | 2358 | 38497 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3100 | 4 | 3.6 | 1105 | 5423 |
| Intel Core i5 9600K | 6 | 3.7 | 1187 | 6596 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3300X | 4 | 3.8 | 1299 | 6787 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 2600X | 6 | 3.6 | 1094 | 7523 |
| Apple M1 | 8 | 3.2 | 1528 | 7799 |
| Apple M2 | 8 | 3.5 | 1701 | 8538 |
| AMD Threadripper 1900X | 8 | 3.8 | 1005 | 8979 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600 | 6 | 3.6 | 1245 | 9073 |
| Intel Core i7 9700K | 8 | 3.6 | 1285 | 9428 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600X | 6 | 3.8 | 1323 | 9526 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600XT | 6 | 3.8 | 1330 | 9945 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 2700X | 8 | 3.7 | 1102 | 10140 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5500 | 6 | 3.6 | 1372 | 10710 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600X | 6 | 3.7 | 1593 | 11201 |
| Intel Core i5 11600K | 6 | 3.9 | 1564 | 11277 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600 | 6 | 3.5 | 1472 | 11429 |
| Apple M1 Pro | 10 | 3.2 | 1543 | 12170 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3700X | 8 | 3.6 | 1345 | 12195 |
| Intel Core i5 12400 | 6 | 2.5 | 1647 | 12344 |
| Apple M1 Max | 10 | 3.2 | 1555 | 12422 |
| Intel Core i9 9900K | 8 | 3.6 | 1343 | 12470 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5980HS | 8 | 3.0 | 1538 | 12844 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3800XT | 8 | 4.2 | 1355 | 12955 |
| Intel Core i7 10700K | 8 | 3.8 | 1345 | 13302 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3800X | 8 | 3.9 | 1346 | 13848 |
| Intel Core i9 9900X | 10 | 3.5 | 1182 | 13994 |
| Intel Core i9 10900X | 10 | 3.7 | 1145 | 14312 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700G | 8 | 3.8 | 1535 | 14350 |
| Intel Core i9 9920X | 12 | 3.5 | 1067 | 14793 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 8 | 3.4 | 1491 | 15003 |
| Intel Core i7 11700K | 8 | 3.6 | 1595 | 15011 |
| AMD Threadripper 1920X | 12 | 3.5 | 1054 | 15038 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | 6 | 4.7 | 1951 | 15204 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800X | 8 | 3.8 | 1596 | 15228 |
| Intel Core i9 11900K | 8 | 3.5 | 1671 | 16211 |
| Intel Core i9 10850K | 10 | 3.6 | 1367 | 16820 |
| Intel Core i5 12600K | 10 | 3.7 | 1918 | 17660 |
| Intel Core i9 9960X | 16 | 3.1 | 1075 | 17953 |
| Intel Core i9 10900K | 10 | 3.7 | 1415 | 18034 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3900XT | 12 | 4.1 | 1354 | 18511 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3900X | 12 | 3.8 | 1312 | 18682 |
| AMD Threadripper 2950X | 16 | 3.5 | 1135 | 18797 |
| AMD Threadripper 1950X | 16 | 3.4 | 1027 | 19635 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7700X | 8 | 4.5 | 1969 | 19910 |
| Apple M1 Ultra | 20 | 3.2 | 1570 | 21740 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900X | 12 | 3.7 | 1670 | 22046 |
| Intel Core i7 12700K | 12 | 3.6 | 1939 | 23488 |
| Intel Core i5 13600K | 14 | 3.5 | 2021 | 24528 |
| Intel Core i9 10980XE | 18 | 3.0 | 1063 | 25490 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3950X | 16 | 3.5 | 1406 | 26375 |
| Intel Core i9 12900 | 16 | 2.4 | 1988 | 26454 |
| Intel Core i9 12900F | 16 | 2.4 | 1988 | 26455 |
| Intel Core i9 9980XE | 18 | 3.0 | 1114 | 27093 |
| AMD Threadripper Pro 3955WX | 16 | 3.9 | 1401 | 27175 |
| Intel Core i9 12900K | 16 | 3.2 | 2003 | 27483 |
| Intel Core i9 12900KS | 16 | 3.4 | 2082 | 27796 |
| Intel Xeon W-3275 | 28 | 3.4 | 1107 | 28051 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5950X | 16 | 3.4 | 1684 | 28782 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7900X | 12 | 4.7 | 2034 | 29358 |
| AMD Threadripper 2990WX | 32 | 3.0 | 1005 | 29651 |
| Intel Core i7 13700K | 16 | 3.4 | 2117 | 31069 |
| Intel Xeon W-3175X | 28 | 3.8 | 1112 | 31350 |
| AMD Threadripper 3960X | 24 | 3.8 | 1307 | 34932 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 16 | 4.5 | 2059 | 38165 |
| AMD Threadripper PRO 5965WX | 24 | 4.0 | 1498 | 40535 |
| Intel Core i9 13900K | 24 | 3.0 | 2275 | 41012 |
| AMD Threadripper Pro 3975WX | 32 | 3.5 | 1244 | 43450 |
| AMD Threadripper 3970X | 32 | 3.7 | 1308 | 46874 |
| AMD Epyc 7702P | 64 | 2.0 | 993 | 48959 |
| AMD Threadripper PRO 5975WX | 32 | 4.0 | 1475 | 53977 |
| AMD Threadripper PRO 3995WX | 64 | 2.7 | 1231 | 73220 |
| AMD Threadripper PRO 3995WX | 64 | 2.7 | 1231 | 73220 |
| AMD Threadripper 3990X | 64 | 2.9 | 1262 | 75671 |
| AMD Threadripper PRO 7995WX | 96 | 2.5 | 1927 | 100295 |
| CPU Name | Cores | GHz | Single Score | Multi Score |
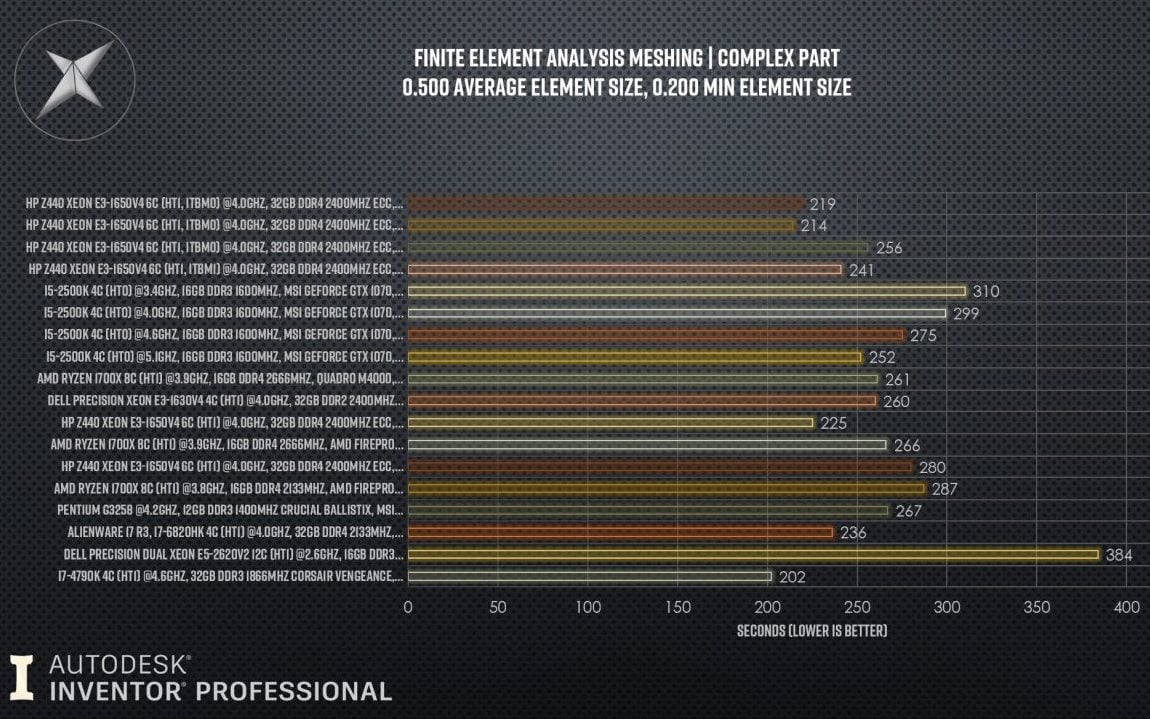
Look at these Inventor Benchmarks of Finite Element Analysis Meshing. High-Core-Clocks with High Turbo-Boost Clocks win all the way (Lower is better):
Here are some Revit Benchmarks. Again, in Single-Threaded Workloads, a CPU with a high Core-Clock (IPC) wins, in multi-threaded workloads such as Rendering, more Cores win.
Performance relative to an i7 7700K that has 4,5GHz Boost Clock, 4 Cores, 8 Threads
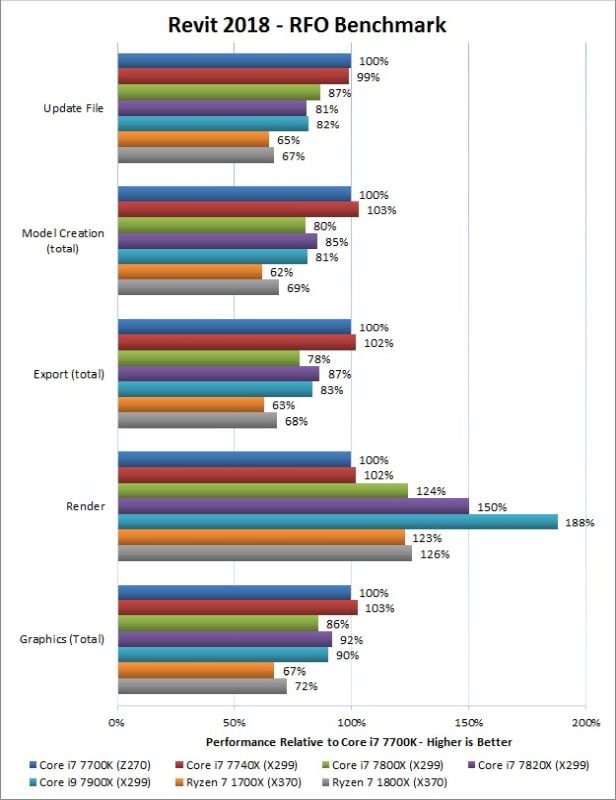
Image-Source: Pugetsystems
These Autocad 2D and 3D Performance Benchmarks were taken with the Cadalyst Benchmark Tool and show how high core-clocks win every time.
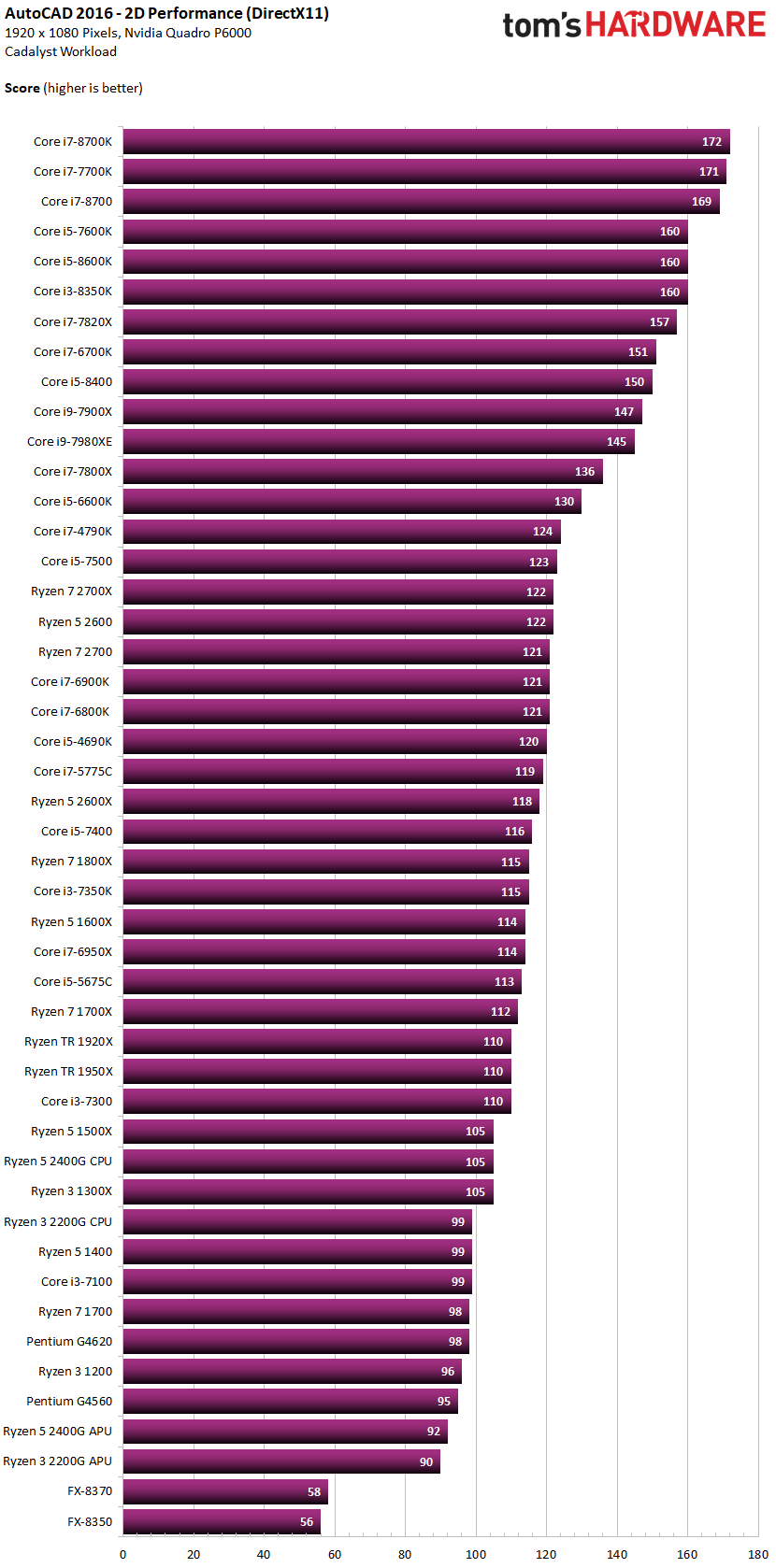
Image-Source: toms hardware
The 3D Performance Benchmarks have high-clocking CPUs at the top of the ranking too:
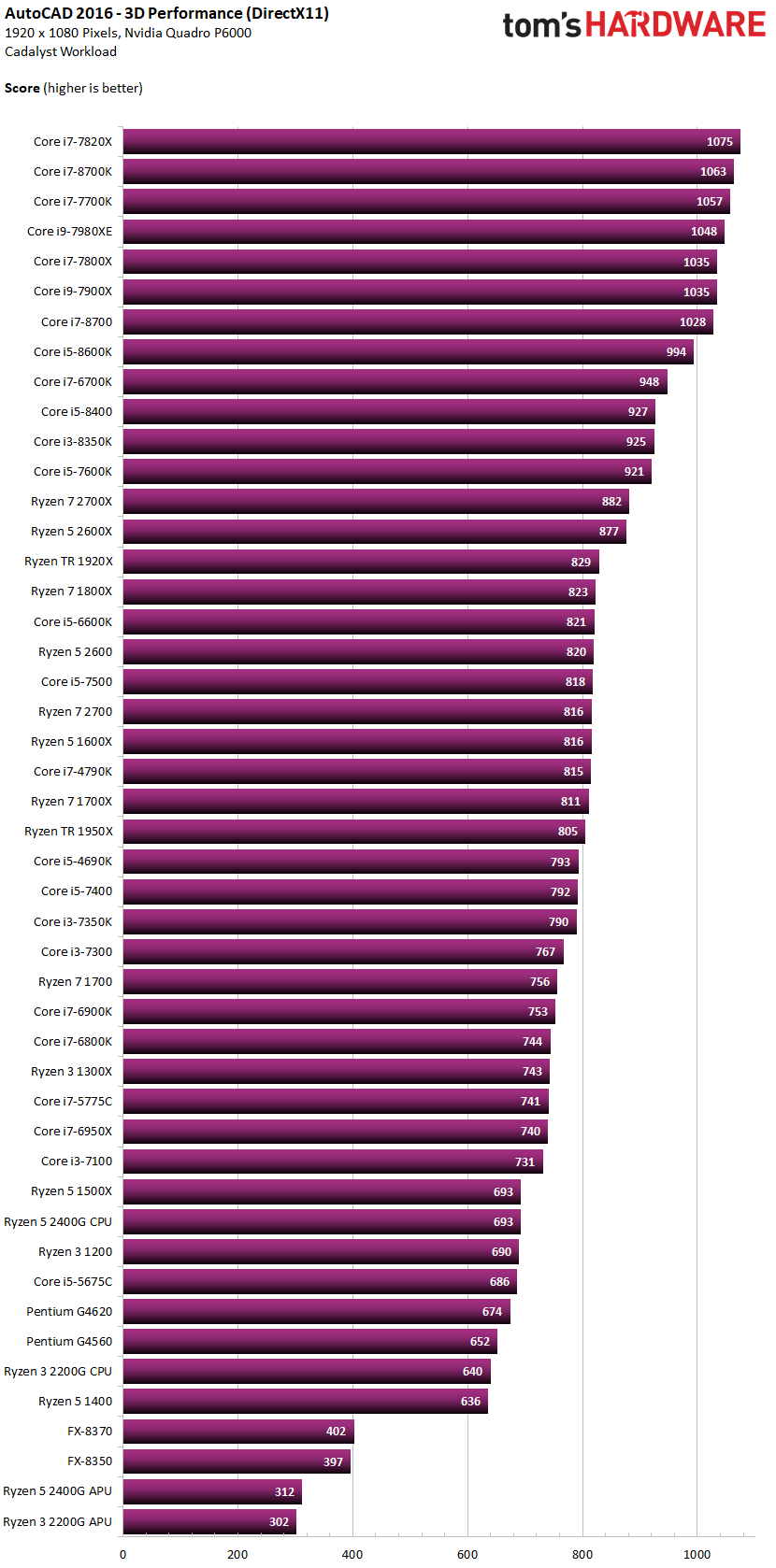
Image-Source: toms hardware
And one last CPU Benchmark for Solidworks, confirming what we have already seen:
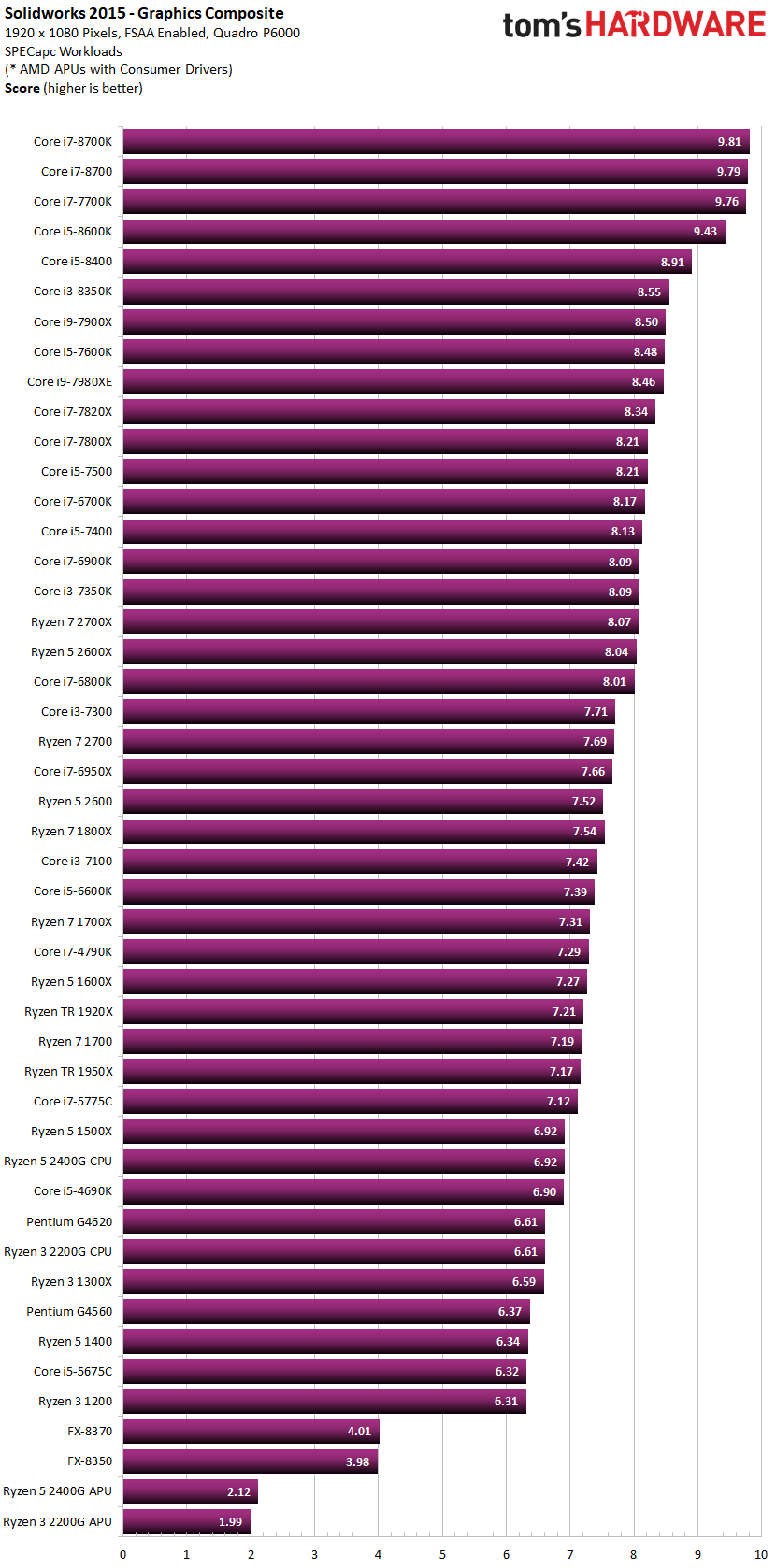
Image-Source: toms hardware
CPU Core Clocks and IPC (Instructions per Cycle) are so important because many tasks cannot be parallelized.
Either because the Software’s Codebase is old and hasn’t been updated or optimized (for parallelization) in a long time, or because certain tasks just can’t be parallelized, because of things like dependencies.
Here’s an example: You are modeling a House in Revit or Sketchup and have your Scene nicely optimized in a non-destructive hierarchical structure.
It looks a bit like this:
- House Wall Extrusion
- Room1
- Window Boolean
- Edge Bevel
- screw Booleans on Edge Bevel
- Edge Bevel
- Window Boolean
- Room1
Now we will thicken the House Wall extrusion a bit.
We have 5 different Objects and would think that having a CPU with, say, 5 Cores would speed up the thickening of the House Wall Extrusion, because every core can work on one object, right?
Image-Credit: Sketchup Help
Wouldn’t that speed up things nicely?
It would, but unfortunately, because the Objects depend on each other as they are in a hierarchical chain, a single CPU Core will have to step through this chain from the topmost hierarchical element first and then move towards the deeper Elements of the hierarchy – one by one.
There is no way the “screw Booleans” can already be calculated before the Edge Bevel has been finished processing and so on. Because of dependencies.
A single CPU-Core will have to work through the entire hierarchical chain by itself.
A single CPU Core will have to first calculate the thicker Wall Extrusion, after that it can calculate the Window Boolean, then the Edge Bevel on The Window Boolean, then the Edge Bevel on that Window Boolean Edge, and only after all of these have been stepped through can the CPU calculate the screw Booleans that are in the Edge Bevel.
All of the other CPU Cores will wait idly during this because such a task can’t be parallelized and offloaded on to multiple Cores.
And this is an example that is quite simple, made for easy understanding. What usually goes on inside a CAD Software is much more complex.
So, long story short: We need a high clocking CPU, that optimally has a nice Boost Clock on one or more cores, to be able to actively work as fast as possible with a responsive and snappy Viewport in CAD Applications.
Here are our CPU recommendations that will bring the most performance to your active work in CAD:
These are all high-clocking CPUs that will give you a smooth working experience within your CAD Application.
What about Xeon or other “professional” CPUs?
What’s the deal with Xeon? It seems to be recommended very often from CAD Software Developers, so it should perform well, right?
Well, the thing with Xeon is, you usually trade Software and Driver certification, official Support, and a high Price for Performance.
Intel Xeons are a lot pricier than the CPUs I listed above, their clocks are lower, IPC is lower & the Turbo Boost Clocks are lower.
BUT, Xeons have ECC Memory Support (Error Correcting memory) that can in very rare cases make your CAD Software more stable.
Also, oftentimes CAD Software Developers only offer support when you actually have an officially supported CPU (such as a Xeon) and not a mainstream or High-End-Desktop CPU.
So if you absolutely need reliability and need immediate support for your systems, then you would have to go the Xeon Route for many of the top-tier CAD Apps out there.
Then again, if you value performance over reliability and can support and troubleshoot on your own, you should be getting a performance CPU as mentioned above, such as the Intel i7, i9 or AMD Ryzen / Threadripper CPUs.
Best Graphics Card for CAD Software
Let’s shed some light on the Quadro vs. Geforce debate:
The Benchmarks will support my writing: Nvidia’s Geforce GTX or RTX Cards are faster in almost all CAD Benchmarks. Autocad, Inventor, Solidworks, Revit you name it.
BUT, professional GPUs such as Nvidia’s Quadro Cards have other things to offer.

They have different Drivers than their mainstream counterparts which enable some features in various CAD apps. Take Solidworks for example: It has a feature called RealView, which is only supported on Pro-GPUs.
Also, the question of Official Vendor Support should not be neglected.
Many CAD Application Vendors only offer support if you use Hardware that has been certified by them, and this certified Hardware consists of mostly professional-grade Components like Nvidia’s Quadro Series or AMD’s Radeon Pro GPUs.
Ask yourself, do you need specific features (e.g. in Solidworks) that are only supported on Pro-GPUs, or do you need official vendor support?
If it’s just your own Workstation you have to worry about and you can troubleshoot on your own and want the fastest experience possible and would like to save some money (because Pro-GPUs are so much more expensive) go with a Geforce GTX or RTX GPU, or an AMD Mainstream GPU.
An Nvidia RTX 2080Ti leads in performance against most Pro-GPUs in many Benchmarks such as the AutoCAD Benchmark below and costs a lot less.
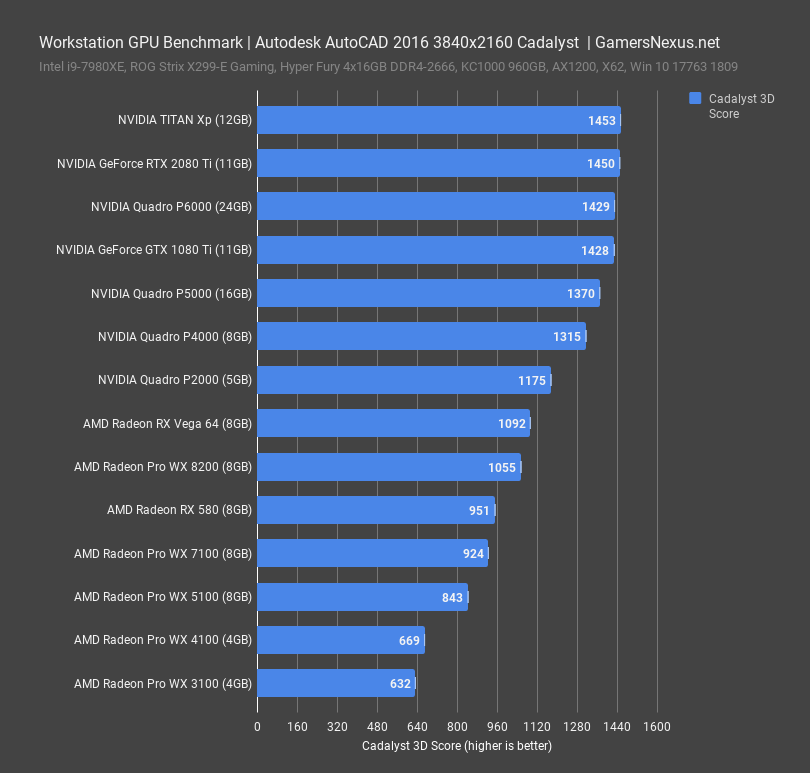
Image-Credit: gamersnexus.net
That said, Solidworks is a bit of a special case: It does benefit from Quadro cards. It seems this Software’s code-base has been well optimized to make use of the additional Features that Nvidia Quadros have to offer (Or mainstream GPUs have been artificially crippled).
If you do want to go with a Quadro, these Benchmarks by Pugetsystems will show you the performance of current GPUs:
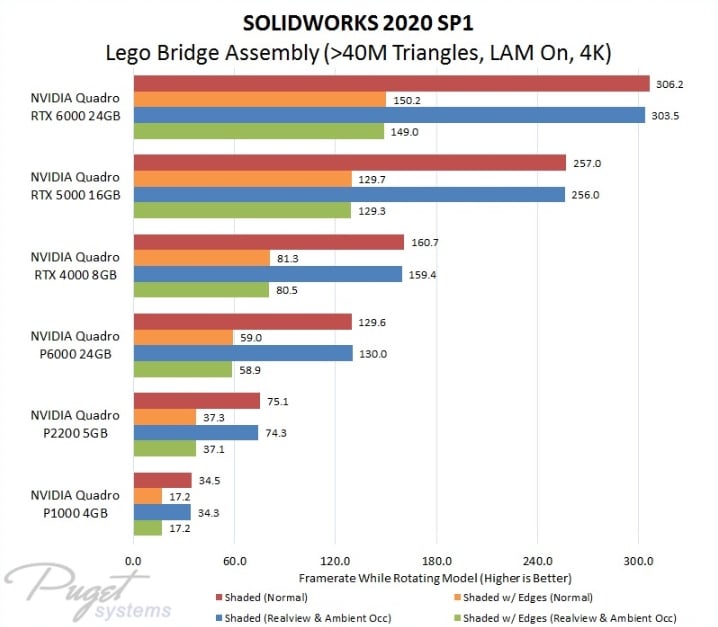
Image-Credit: Pugetsystems
Our GPU recommendations for CAD Software:
Nvidia GPUs for Animation
- Nvidia Quadro Series (Recently renamed to A-Series)
- Nvidia RTX 3090
- Nvidia RTX 3080
- Nvidia RTX 3070
- Nvidia RTX 3060 Ti
AMD GPUs for Animation
- AMD Radeon Pro Series
- AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT
- AMD Radeon RX 6800
Now that we’ve discussed the most controversial Parts of a CAD Computer let’s move on to some basics:
Best Motherboard for CAD Applications
The Motherboard won’t influence your performance all that much, but you should make sure it supports all the features you need and matches the Hardware that you are going to plug into it.
Of course, you should match the Motherboard Socket to the CPU you chose earlier. Get an LGA1700 Motherboard (Z690 Chipset) for an Intel Core i9 12900K (or same Generation) CPU, and an AM4 Motherboard (X570 Chipset) for an AMD Ryzen 5900X CPU.

Image Source: MSI
Other features you should look out for are the number of PCIe-Slots that you can plug Graphics Cards into, the number of USB connectors, the amount RAM Slots as well as the number of Storage Devices such as M.2 Slots you have available to use.
For AMD Ryzen 9 5900X, which I currently recommend highly for CAD Apps, you will need an AM4 Motherboard such as the MSI Tomahawk x570.
Do give our Motherboard Guides a quick read, if you are having trouble picking a suitable one. We have a Motherboard Guide for Intel CPUs and AMD CPUs.
Best RAM (Memory) for CAD Software
CAD Workloads are very similar to working in 3D Applications like Cinema 4D or Maya.
The amount of RAM needed depends very much on how complex your projects and assemblies are and how many projects you have opened at the same time.
Also, if you tend to have more RAM-hungry Applications in addition to your CAD Software open at the same time, you should make sure you have sufficient RAM.
Running Windows 10, for example, and having Chrome, an E-Mail Program, some other DCC Software like Photoshop and Illustrator, and a Word-Processing App open at the same time in addition to your CAD Software will surely eat away at your RAM much more than when you have only one App open at a time.
It is “ease of use” that we are looking for, and closing down other Applications just so we can use our CAD Software is not very efficient.
For lighter CAD work you should be looking to buy at least 16GB of RAM.
With more complex assemblies or when you are using multiple Apps at the same time, you should be leaning towards 32GB or even 64GB of RAM.

Image-Source: G.Skill
For Mainstream or HEDT CPUs such as the Intel i7, i9, or Ryzen / Threadripper CPUs, I recommend the Corsair Vengeance LPX DDR4 RAM that comes in all sorts of Memory capacities.

Memory Clock Speed can influence your CPU’s performance and it is advised to aim for RAM clocked at 3200Mhz or higher.
Best SSD / HDD / Storage for CAD Work
Assemblies and other Project Files can get quite big, especially on complex projects. You will be happy to have enough storage space to keep all of your projects saved in multiple revisions – Additionally, a fast drive for loading and saving your Projects will keep you working longer and waiting less.
The currently best type of storage Device for most PC-workloads, including CAD workloads, is the NVMe M.2 SSD.
This stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express M.2 (the form factor) Solid State Drive and basically is an SSD that has been further developed to:
- Be smaller
- Use a faster interface and
- Be much faster in reading and writing data.

Image-Credit: Samsung
You can plug an NVMe SSD into the Motherboard without needing any cables. It is about the size of a stick of chewing gum, and about 5 times as fast as a regular SATA SSD, and about 25x faster than a mechanical HDD.
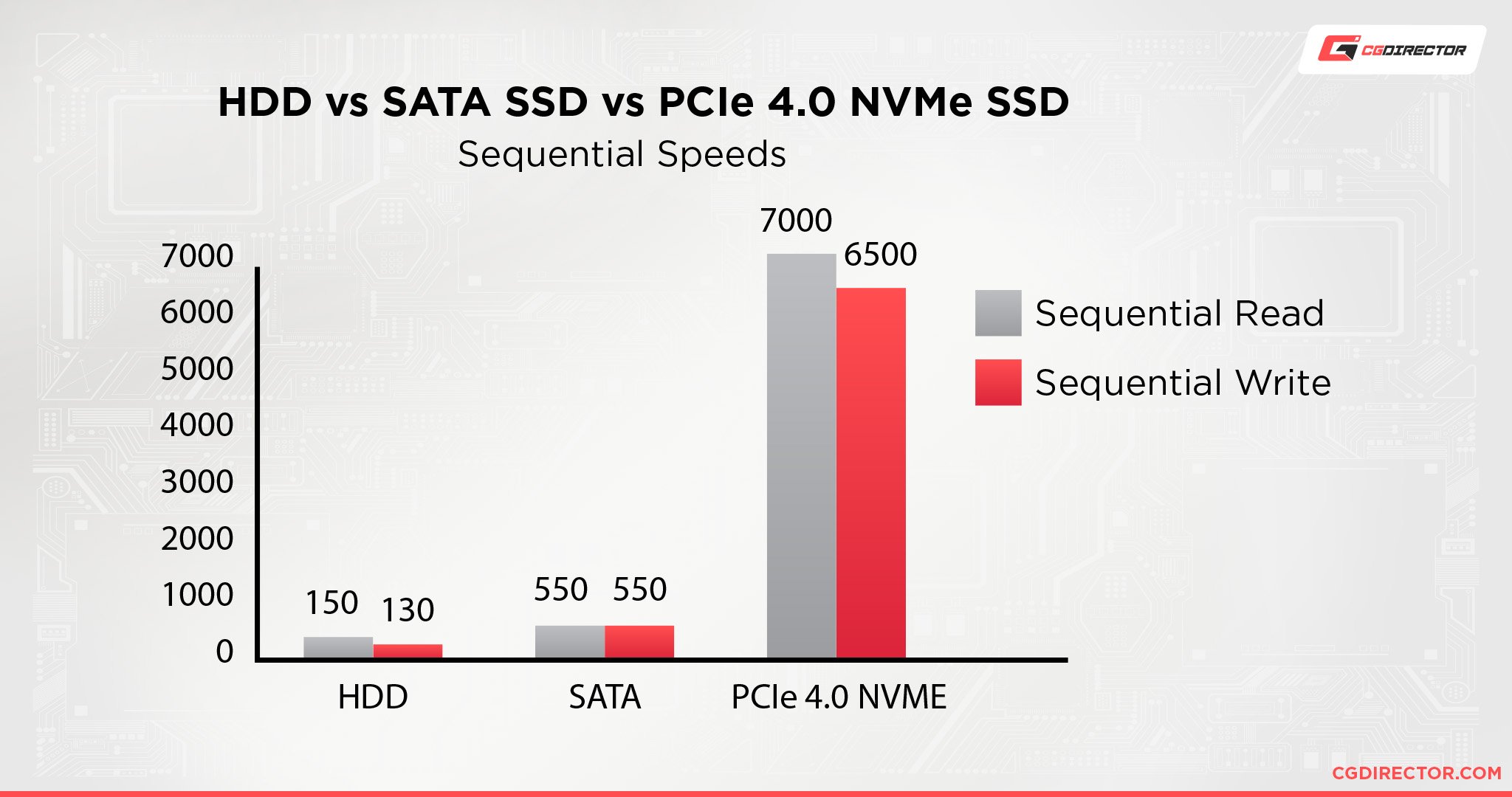
I recommend buying an NVMe SSD from the Seagate FireCuda 530 Series, which comes in sizes from 500GB – 2TB.
Of course, NVMe Drives are somewhat more expensive than HDDs or SATA SSDs and it’s best to get both – A smaller NVMe SSD for active projects, apps, and the OS. And a large HDD for Backups and Archiving.
For High-Performance CAD workloads, an NVMe SSD should be a standard on your buy-list. Do check out our NVMe SSD Guide to see more of the available options.
Best PC-Case for CAD Work
Your PC’s Case, of course, will not influence the performance of your CAD Build in any way. Well maybe in terms of air-flow, but that can usually be neglected as CAD Work doesn’t tend to make your CPU or GPU overheat all that fast (unless you’re doing some heavy rendering).
There are lots of Cases out there in all kinds of Colors, Sizes, and from many different Brands.
There is not much you can do wrong here. Check your Motherboard Form-Factor (e.g. M-ATX or ATX or E-ATX) and make sure your case can fit this Motherboard size. The most common size is ATX and you’ll find a gazillion options to choose from.
A nice Case that I keep coming back to is the be quiet! Silent Base 601, which looks professional and has some noise-dampening features that will make your CAD PC quieter.

Image-Source: be quiet
Best PSU for CAD
The Power Supply Unit should have sufficient Wattage to be able to power your Components.
If you are unsure as to how much Watts your selected Components actually need, check out this easy to use Wattage-Calculator over on beQuiet’s Website.
Some reliable brands to look out for are Corsair, beQuiet, Seasonic, and EVGA that I have tested extensively.
We have a Guide to finding the best modular PSU’s here if you need some more specific recommendations.
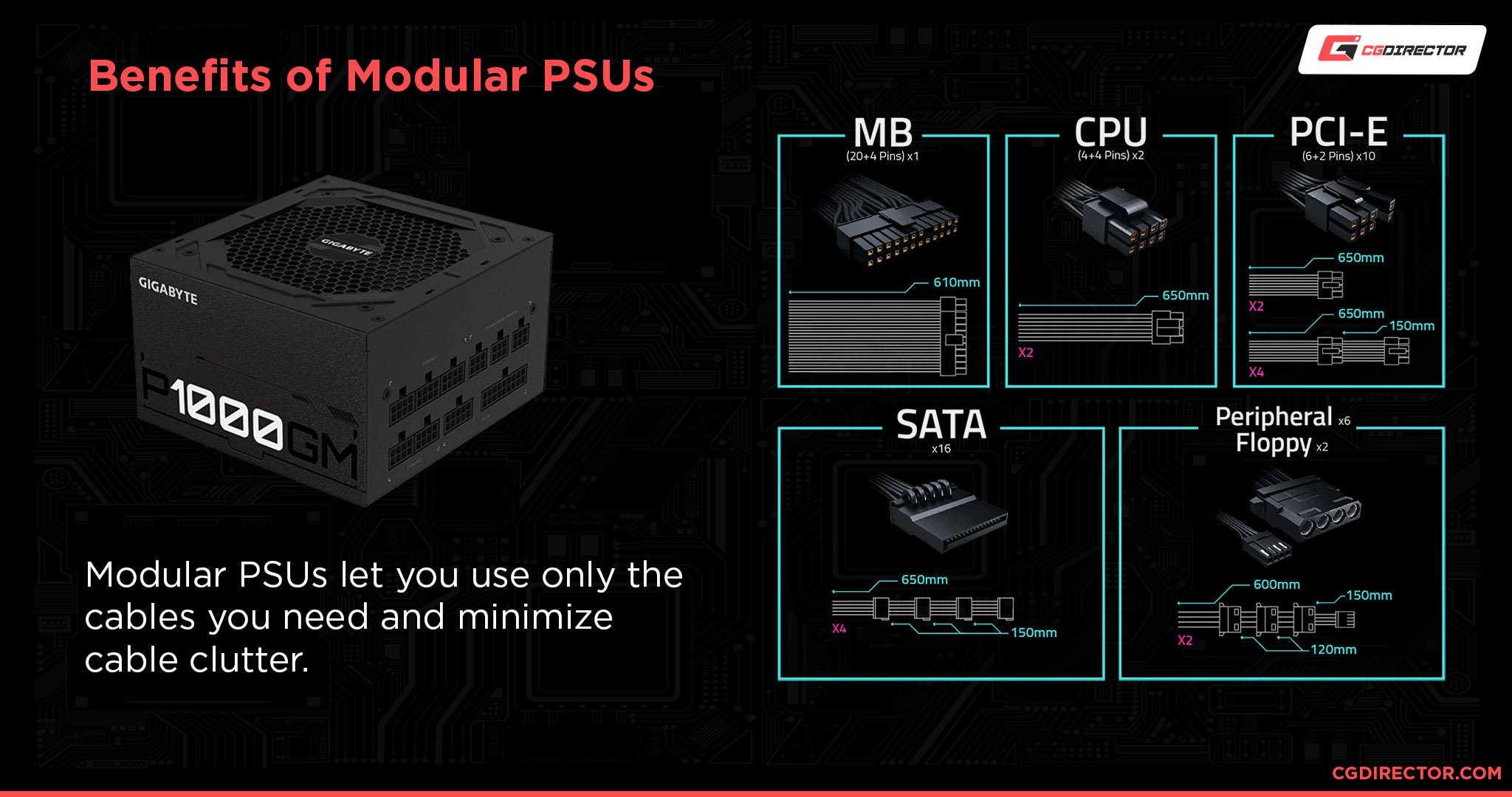
I recommend buying a somewhat stronger PSU than you currently need. This way you can upgrade to more powerful components in the future without having to buy a new PSU.
Completed & compatible PC Builds for CAD
That’s about it for the Main Hardware Components needed for a great Computer for CAD Workloads!
Let’s take a look at some finished Builds at different price points, that will work well with CAD Apps such as Autocad, Solidworks, Inventor, Revit, and lots of others.
Keep in mind, that these are Performance builds and not Reliability/Support Builds. If you are responsible for CAD Computers at a large company you might want to trade performance for reliability and support, but that, of course, is up to you.
Performance Builds: Best Computers for CAD
Best Computer for CAD, AMD ~1000$
Some Build notes:
AMD’s 3rd Gen Ryzen CPUs bring a lot of bang for your buck to the table and will make sure to accelerate your active work and Viewport Performance. The AMD Ryzen 5 3600XT sports 6 Cores / 12 Threads that clock fairly high and can blaze through some of your renders and simulations in no time.
At this price point, the Nvidia GTX 1660 Ti 6GB, 16GB of DDR4-3200 RAM, and the Adata XPG NVMe SSD easily step up to the task of making this a great budget PC-Build for CAD.
Best Computer for CAD, AMD ~1700$
Some Build notes:
Stepping up the performance at 1700$, this configuration brings an 8-Core Ryzen 5800X CPU with it, which clocks higher and sports more cores for faster active work and rendering. I added a third-party CPU Cooler, the beQuiet Dark Rock Pro 4 to the Build List, which is one of the best Air Coolers to keep the CPU nice and cool, even during sustained loads.
The Nvidia RTX 3070 Graphics Card is a workhorse that will enable you to do some fast GPU rendering and will handle any OpenGL/Viewport related tasks without any trouble.
32GB of RAM and a 1TBNVMe SSD make sure you can work on complex CAD Projects and have multiple of them opened at the same time.
Best Computer for CAD, AMD ~2600$
This 2600$ AMD PC Build brings with it all the bells and whistles that you can think of. Although the AMD Ryzen 5950X CPU has 16 Cores those cores clock even higher than lower-core CPUs and will make your active work snappy and smooth.
The GPU is an Nvidia RTX 3080 which is a beast of a Graphics Card that will blaze through your GPU Renders in no time. True, if GPU rendering or other GPU-intensive tasks aren’t part of your everyday work, this might be a bit overkill, but for those who can make use of it, it’s a time-saver.
64GB of RAM makes sure you’ll almost never have to close down a Project or Software again and a 2TB SSD makes sure you have enough space for lots of Programs and Projects.
Reliability Build: Best Computer for CAD
Best reliability Computer for CAD, Intel XEON / Nvidia Quadro ~6350$
- CPU: Intel Xeon W-2145, 8x 3.70GHz
- CPU-Cooler: be quiet! Dark Rock Pro 4
- Motherboard: ASUS WS C422 Pro/SE
- Memory: 2x (or 4x) Kingston Server Premier DIMM 16GB, DDR4-2666, CL19-19-19, reg ECC (KSM26RS4/16HAI)
- Storage: Samsung – 970 Evo 500GB M.2-2280 Solid State Drive
- GPU: PNY Quadro P6000, 24GB GDDR5X, DVI, 4x DP
- Case: Fractal Design Define S – ATX Midi Tower
- Power Supply: Corsair Professional Series Platinum AX760 760W
This is an excellent Reliability / Durability / Stability Computer for CAD Applications with the potential of being granted Support from more picky Software Manufacturers.
The Xeon gets you ECC RAM Support and the Quadro offers Drivers with additional Features in many CAD Apps as well as 10bit Monitor Color output.
The price tag sure is hefty, but that is what you pay for reliability.
Custom PC-Builder Tool
Head on over to the PC-Builder Tool that lets you configure your Computer at custom price points for all kinds of purposes. It suggests parts that work well together and gets the maximum performance out of your budget.
Build your own Computer
Assembling your own PC has many benefits. It is much cheaper to buy the individual hardware components and assemble them on your own.
It is lots of fun, easy and you learn a lot.
With that knowledge, you should be able to troubleshoot any problems that might arise later-on yourself, without having to bring your computer to a shop to have it fixed.
You can upgrade parts on your own when newer and faster hardware is available and you learn a lot about how computers work, which never hurts!
Start by taking a look at what parts you need for building your own Computer.
After that, here is our PC Build Guide for you to read or, if you are the visual type, here is an easy to follow Video Tutorial on how to build/assemble your own Computer:
Best Laptops for CAD Software such as Autocad, Solidworks, Inventor, or Revit
So what about Laptops? We have been talking about Desktop Computers all this time but fortunately, everything we discussed above can also be applied to a Laptop.
Whether you’re an engineering student looking for a new Laptop or a seasoned professional, the theory behind what is important in choosing a high-end Laptop for CAD Workloads is the same as in desktop Computers for CAD.
We will need a high-clocking CPU, an Nvidia GTX or RTX GPU, 16-32GB of RAM, and a fast M.2 SSD.
As the Hardware components in Laptops are usually supposed to draw much less power, the components will not reach the performance of a Desktop PC.
But that is to be expected from such a small enclosure. In a Laptop, you get the benefit of Mobility but trade it for performance.

We will differentiate between performance vs reliability/support, as both the Xeon CPUs and the Quadro GPUs are available for Laptops.
Best Performance Laptop for CAD Software
If it’s Performance you are after, you will want to lean towards a high-clocking CPU and a higher-end GPU such as the GTX 2070 as you will find in the following Laptop:
The GIGABYTE Aero 15 OLED 15″ Ultra Slim Laptop

Image-Credit: Gigabyte
The Specifications on this Gigabyte Laptop are:
- CPU: i7-9750H
- GPU: GeForce RTX 2070 with 8GB of VRAM
- RAM: 16GB RAM
- SSD: 512GB PCIe SSD
- Win 10 Pro
- 15,6″ / 4K IPS Screen with a FullHD Resolution
Some notes on this Laptop:
The Gigabyte Aero 15 OLED is the newest of a long line of excellent Laptops for Content Creators. It comes with an excellent 15,6″ 4K IPS Screen which performs admirably for visually demanding work.
The Nvidia RTX 2070 is a top-tier GPU with 8GB of VRAM and the Intel i7-9750H will make sure your active work and viewport experience is as smooth as it can get in a mobile form factor. The great thing is, it sports a Numpad, which is very rare in 15″ Laptops – I personally use the Numpad all the time, but you might feel differently.
If the Gigabyte hasn’t hit your sweet spot yet, here are two more great choices:
- ASUS ROG Zephyrus G15 (2020) with an AMD 4800H CPU and an Nvidia 1660Ti, which is quite affordable.
- Razer Blade 15 Series Laptops, which are quite popular among Content Creators and Gamers alike.
Best Reliability / Support / Stability Laptop for CAD Software
The Lenovo ThinkPad P52 (2018) 15.6″ Business Laptop.
Image-Source: Lenovo
The Specifications on this Gigabyte Laptop are:
- CPU: Xeon E-2176
- GPU: Quadro P2000 (4GB)
- RAM: 16GB RAM
- SSD: 512GB PCIe SSD
- Win 10 Pro
- 15,6″ IPS Screen with a FullHD Resolution
Some notes on this Laptop:
The Lenovo ThinkPad P52 has a 6-Core Intel Xeon CPU that boosts up to 4.4GHz. With 16GB of Ram, an Nvidia Quadro P2000 GPU, and a PCIe-M.2 SSD you will get the Reliability Workstation Experience inside a mobile Form factor.
Answers to frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is a CAD Workstation?
A CAD Workstation is no different from a regular Desktop PC that consists of hardware components that run CAD workloads well. It consists of the same parts that anyone can buy and put into their PC, but for marketing purposes, the name “CAD Workstation” has a professional feel to it and is therefore used to target more wealthy spenders.
How much RAM do you need for CAD?
You’ll need a minimum of 8-16GB of RAM for simple CAD Projects and should consider 32-64GB if your CAD Projects and Models become more complex or if you’re doing simulation and rendering.
Is Intel or AMD better for CAD?
Intel leads in single-core performance, while AMD is more power-efficient and leads in multi-core performance. Because most CAD tasks involve viewport interaction and real-time interaction, Intel currently is the better option for CAD workloads (marginally). This changes every few months though when new CPUs are released.
Is a Mac good for CAD Software?
Apple has caught up to the PC competition in recent years and you’ll find Mac to perform very similarly in most CAD software.
So, yes, a Mac is a viable alternative to a PC for doing CAD work. Because not every software has been ported to Mac (M1, Metal, or otherwise) yet, though, you should make sure to check which software is supported on Mac before you make a decision.
Can you run AutoCAD on an i3 or Celeron CPU?
You can but it won’t be an enjoyable experience. Intel Core i3 and Celeron CPUs are targeted at the budget market for a reason and it’s not for giving away performance for cheap. You can certainly use it to work on simple projects, though.
Over to you
That’s about it! What Computer or Laptop for CAD are you thinking of buying? Let us know in the comments or ask us anything in our expert forum!



![Laptop vs. Desktop PC for Work – Which should you choose? [UPDATED 2024] Laptop vs. Desktop PC for Work – Which should you choose? [UPDATED 2024]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2022/05/Laptop-vs.-Desktop-Workstations-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Best PC / Workstation for Autodesk Revit [Updated Guide] Best PC / Workstation for Autodesk Revit [Updated Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2020/10/Best-PC-for-Autodesk-Revit-Twitter_1200x675-1-594x335.jpg)


256 Comments
24 February, 2025
I looking for best system to run CAD
25 December, 2022
hello and 10x
what is the benefit of using Seagate FireCuda 530 as u suggest?
WD black and Samsung pro 980 aren’t better?
14 November, 2022
Hi. I’m a 4th-year architecture student looking for a new laptop, focusing on BIM-based software like Archicad, Revit, and rendering software like Lumion, V-ray, etc. My budget is Rs 1 Lakh to 1.5 Lakhs. I was thinking to buy the Asus TUF Dash F15 2022 FX517Z with specs- i7-12650H, Nvidia GeForce RTX 3070 with 8GB vRAM, 16 GB RAM, 1 TB storage, and a WQHD display with 165 Hz refresh rate. The reviews say that the screen output is not that great. Are there any suggestions?
14 December, 2022
Hey Divya,
It’s a decent Laptop for your workloads. I can also recommend the MSI Creator M16, the ASUS ROG Strix Scar 15 (2022) Laptop and the HP OMEN 15 Laptop, which should all be in the budget range you mentioned.
Cheers,
Alex
30 September, 2022
Thanks for the article Alex.