TABLE OF CONTENTS
AMD is the only PC component manufacturer that builds both CPUs and dedicated graphics cards for the mainstream PC market. Still, when it comes to GPUs, many do prefer Nvidia.
Even with AMD’s most recent release of their RDNA 2 Radeon RX 6000 series of graphics cards, Nvidia is still regarded by many to be the superior Graphics Card vendor.
But when it comes to CPUs, AMD’s Zen 3 Ryzen processors are currently more popular than Intel’s CPUs and are gaining market share by the day.
Therefore, considering the pairing of an AMD CPU with an Nvidia GPU will only come naturally for many PC builders.
If you agree with this design decision, this article will give you a rundown of the benefits and drawbacks that accompany the combination of an AMD CPU with an Nvidia Graphics Card.
Are Nvidia GPUs Compatible With AMD CPUs?
In short, the answer to this question is a resounding: yes. AMD CPUs are compatible with dedicated graphics cards from both AMD and Nvidia and can synergize just as well with both options.
In other words, no performance issue will be experienced with this type of setup.
That being said, there are some inherent advantages that are innate to the synergy found between central and graphical processors made by the same manufacturer.
Whether these benefits outweigh the utility of Nvidia’s own proprietary technology will depend entirely on your preferences and the purpose of your build.
Are There Any Benefits of Using AMD GPUs with AMD CPUs?
To help you outweigh the upsides and downsides between choosing an AMD or Nvidia GPU – to accompany your AMD CPU – let’s go through the exclusive features each option holds.
AMD for 3D Rendering and Workstations
But before going into any specifics, it must be mentioned that AMD’s GPUs are far more catered to a gaming audience. This is why their features aim more so at enhancing the number of frames per second (FPS) the GPU can render.
Their ray-tracing capabilities are below par, in contrast to the 2nd generation RT cores of Nvidia, so they are not ideal options for most professional 3D rendering workloads.
Additionally, their lack of CUDA cores translates to many 3D Render Engines, like Octane and Redshift being inoperable for these GPUs. ( – at time of writing this article. Both Octane and Redshift are working on AMD GPU support.)
Also, when it comes to content creation and professional editing workloads, the performance of AMD GPUs are severely lacking when compared to their Nvidia counterparts.
Benchmarks by Puget Systems show the flagship $999 Radeon RX 6900 XT trailing the $399 GeForce RTX 3060 Ti when it comes to GPU effects for DaVinci Resolve.
It also falls behind the previous generation GeForce RTX 2080 Ti for Unreal 4.26 ray tracing performance.
Smart Access Memory
The exclusive feature which requires both an AMD CPU & GPU is AMD’s Smart Access Memory (SAM); which works solely between RDNA2 GPUs and Zen 2 or Zen 3 CPUs.
SAM creates an expanded data channel that takes advantage of the CPU PCI Express lanes that the GPU already needs in order to operate.
With the increased bandwidth provided by the PCIe bus, the CPU can access far larger temporary assets from the GPU’s VRAM.
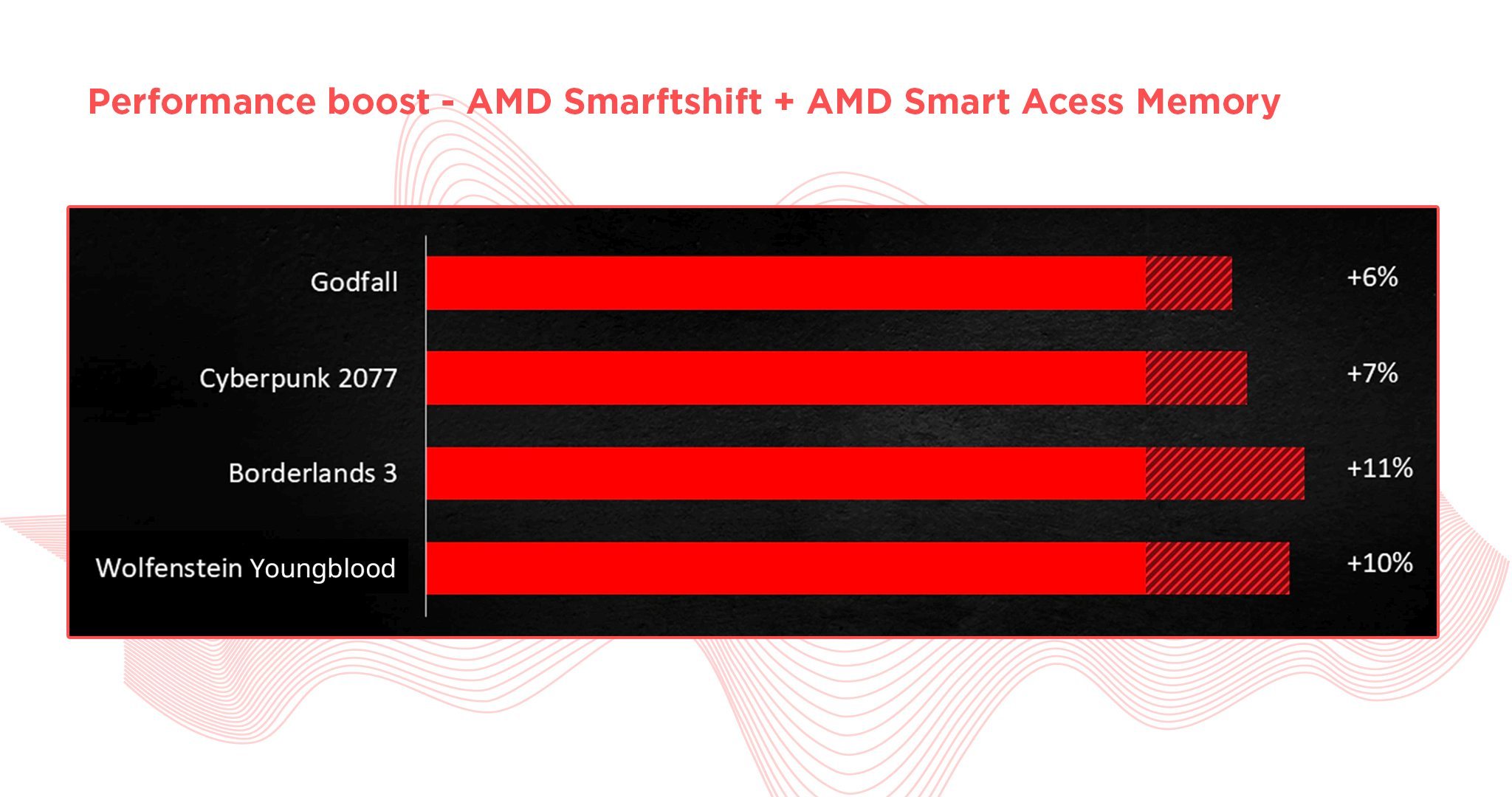
This practically results in an increase in gaming performance; though, depending on the title, there may be a decrease in performance as well.
After testing 22 different games, TechPowerUp found a 2% overall increase in relative performance for the Radeon RX 6800 XT across all resolutions.
Nvidia’s Answer to Smart Access Memory
These concurrent, or full-scale, transfers from the GPU’s VRAM to the CPU – via the use of the bandwidth of PCI Express lanes – are also known as rBAR (Resizable BAR).
Nvidia’s Resizable Bar feature works for both AMD and Intel (10th and 11th generation) CPUs, and even allows support for AMD 400 series chipsets, which SAM does not.
However, rBAR only works for Ryzen 5000 series CPUs and is therefore incompatible with Zen 2 processors.
Another downside is that it currently only supports 17 different gaming titles.
Open Source Drivers
If you are a Linux user that requires graphics-rendering Application Programming Interface (API) support, then you will find AMD’s GPUs to be far more favorable than Nvidia.
Nvidia’s only open-source driver (named “nv”) was deprecated by Nvidia in 2010. On the other hand, AMD’s Catalyst is up-to-date and readily available for both Windows and Linux systems.
Energy Efficiency
If performance per Watt is important for optimizing your setup’s productivity, then certain AMD GPUs may work better for your build.
According to benchmarks carried out by Tom’s Hardware, the RDNA2 Radeon RX 6000 series GPUs were more energy-efficient than equivalently priced Nvidia GPUs.
In fact, in these tests, the Radeon RX 6800 was found to be the most power-efficient GPU – based on performance.
Price Value
One final factor to take into consideration is the price of AMD’s GPUs versus their Nvidia competition.
Depending on the model and task, AMD graphics cards can be found to be more cost-efficient in many cases.
For example, when it comes to gaming performance, the Radeon RX 6800 XT outperforms the GeForce RTX 3080 in cost per frame for every resolution tested.
Are There Any Benefits to Running Nvidia GPUs on Intel CPUs?
In general, the answer to this question is: no. Whether paired with an AMD or Intel CPU, the performance of the GPU itself will not differ.
Nonetheless, there is an argument to be made in regards to which CPU and GPU combination is best to opt for; especially when it comes to Artificial Intelligence performance optimization.
Nvidia’s Tensor Cores, together with Intel’s DL Boost, do provide impressive benchmarks for AI & machine learning applications.
Conclusion
Ultimately, when it comes to choosing a GPU for your build, it hardly matters whether you have an AMD or Intel CPU.
That being said, if you want to maximize your PC’s potential performance for a specific task, even small advantages can go a long way.
Both AMD and Nvidia provide great options for graphical processors.
When it comes to 3D rendering and workstation builds, Nvidia does hold a significant advantage. However, for dedicated gaming PCs, AMD supplies peak 1080p and 1440p performance – especially with their Radeon RX 6900 XT – and far better cost-per-frame performance for 4K gaming (TechSpot).
Answers to frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Can you use an AMD GPU with an Intel CPU?
Yes, AMD GPUs are fully compatible and will run fine with any Intel Processor.
Can you use Geforce Experience with AMD?
Yes, you can use Geforce Experience even on an AMD GPU if it’s new enough and fulfills the requirements. We recommend using AMD’s Adrenaline Software for the best experience on AMD GPUs.
Does CUDA work with AMD?
No, it does not. CUDA is a proprietary technology made to run on Nvidia GPUs only.
Over to you
Are you planning on using an AMD CPU with an Nvidia GPU? Do you need any advice for planning your next PC build’s components?
Feel free to ask us in the comments below, or join our expert forum where you will find a friendly community with a plethora of users!



![Can You Run Two Different GPUs in One PC? [Mixing NVIDIA and AMD GPUs] Can You Run Two Different GPUs in One PC? [Mixing NVIDIA and AMD GPUs]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/03/Can-You-Run-Two-Different-GPUs-in-One-PC-Mixing-NVIDIA-and-AMD-GPU-Twitter-594x335.jpg)


15 Comments
7 June, 2024
Is a intel i5 or ryzen 5 better for overall gaming?
16 February, 2024
Hello, I have an HP with AMD Radeon graphics. For remote work purposes, I need Nvidia card 1050+ U. Are the two compatible and what would be the steps for installing the Nvidia GPU? Thank you!
18 February, 2024
You should be able to add or swap your current GPU for an Nvidia one. What specific type of HP Computer do you have?
25 November, 2022
You’ll need nvidia gpu to use it. what you linked is geforce now which is NOT geforce experience.
Can you use Geforce Experience with AMD?
Yes, you can use Geforce Experience even on an AMD GPU if it’s new enough and fulfills the requirements.
25 November, 2022
Thanks fixed that link! 🙂
Cheers,
Alex