TABLE OF CONTENTS
Clearing your CMOS can help you with a wide array of problems.
It’s a well-known “workaround” that can help with things like hardware compatibility issues, inadequate BIOS settings, post-upgrade woes, and more.
If you’ve stumbled upon an issue that seems too tough to crack, don’t worry – chances are it’s nothing serious… nothing a good old “clear CMOS” method won’t be able to fix.
But, what is CMOS, is it safe to clear it, and should you clear it right away or look for other potential issues instead?
What is CMOS?
CMOS stands for complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor but is often referred to as CMOS RAM and RTC (real-time clock).
CMOS is an onboard, battery-powered chip that’s used inside computers for various things, including time and date settings, and system settings.
The standardized CMOS battery is the 3v CR2032, and it’s capable of lasting around ten years.
Of course, this depends on the use case but, in most scenarios, you will never have to change your CMOS battery.

How can you tell if your CMOS battery’s levels are nearly depleted? It’s simple – your PC won’t be able to keep time and date records or other BIOS settings you have set after shutdowns and your PC is likely to display several CMOS errors when booting up.
CMOS’ Aren’t the Same Anymore
Back in the old days of early IBM computers, CMOS’ were able to store 64 bytes of data in total.
14 bytes were used for time and date storage, and the remaining 50 were used for system settings storage.
We’re talking about low-level settings here, used to power up the board and initialize connected hardware and peripherals.
These days, however, motherboard manufacturers have moved the system (AKA BIOS) settings from CMOS to either the Southbridge or Super I/O chips.
But, if CMOS no longer stores system settings – what does clearing CMOS do in addition to resetting the time and date?
How to Clear CMOS / Reset BIOS?
The thing is, CMOS chips cannot store BIOS settings anymore.
These days, there’s a lot more data to be stored, and CMOS chips’ capacity simply isn’t sufficient.
Instead, board manufacturers now use NVRAM chips which not only have much higher capacity but store data persistently, even when there’s no power source connected to the board.
Even though the CMOS chip no longer stores BIOS settings, modern PCs still have CMOS batteries, and the term “clearing CMOS” is still used for resetting the BIOS.
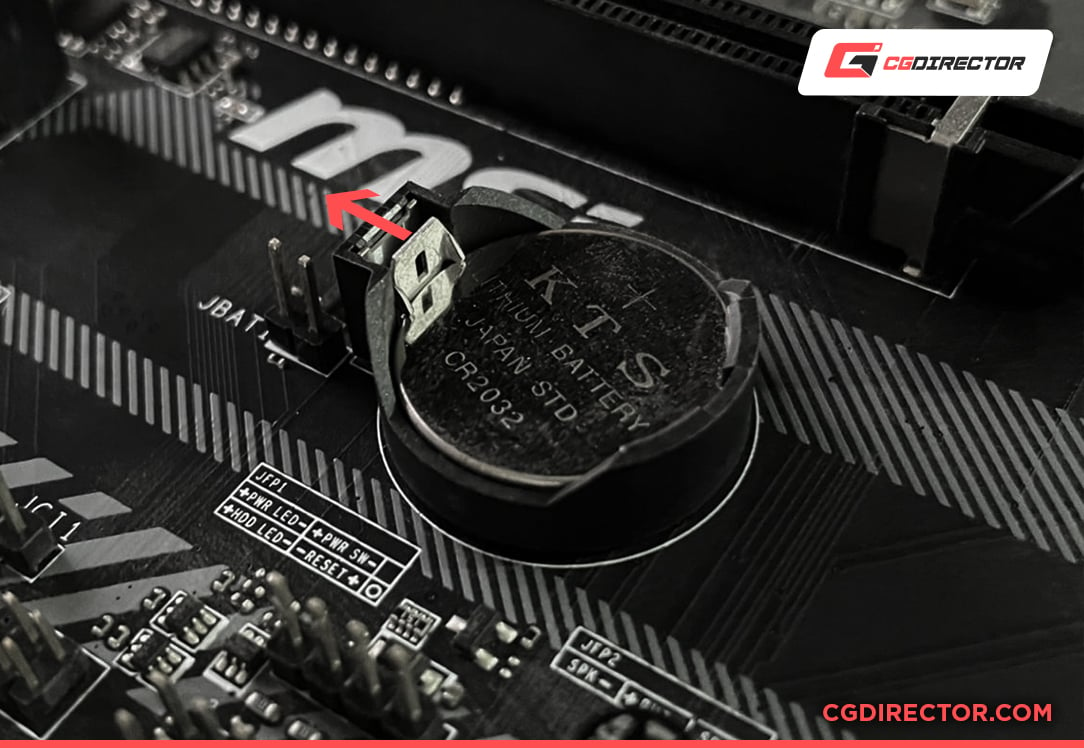
Removing the CMOS Battery
Removing the CMOS battery is still the most common method used to clear CMOS and reset BIOS settings to default values.
This functionality has been kept because of tradition and nothing else.
People are so used to reset their BIOS by removing the CMOS battery that board manufacturers decided to keep this functionality in place.

But, several other ways are just as (perhaps even more) straightforward as this one.
Using the Reset Button
These days, mid and high-end boards typically have reset CMOS/BIOS buttons either on the board itself or the rear I/O.
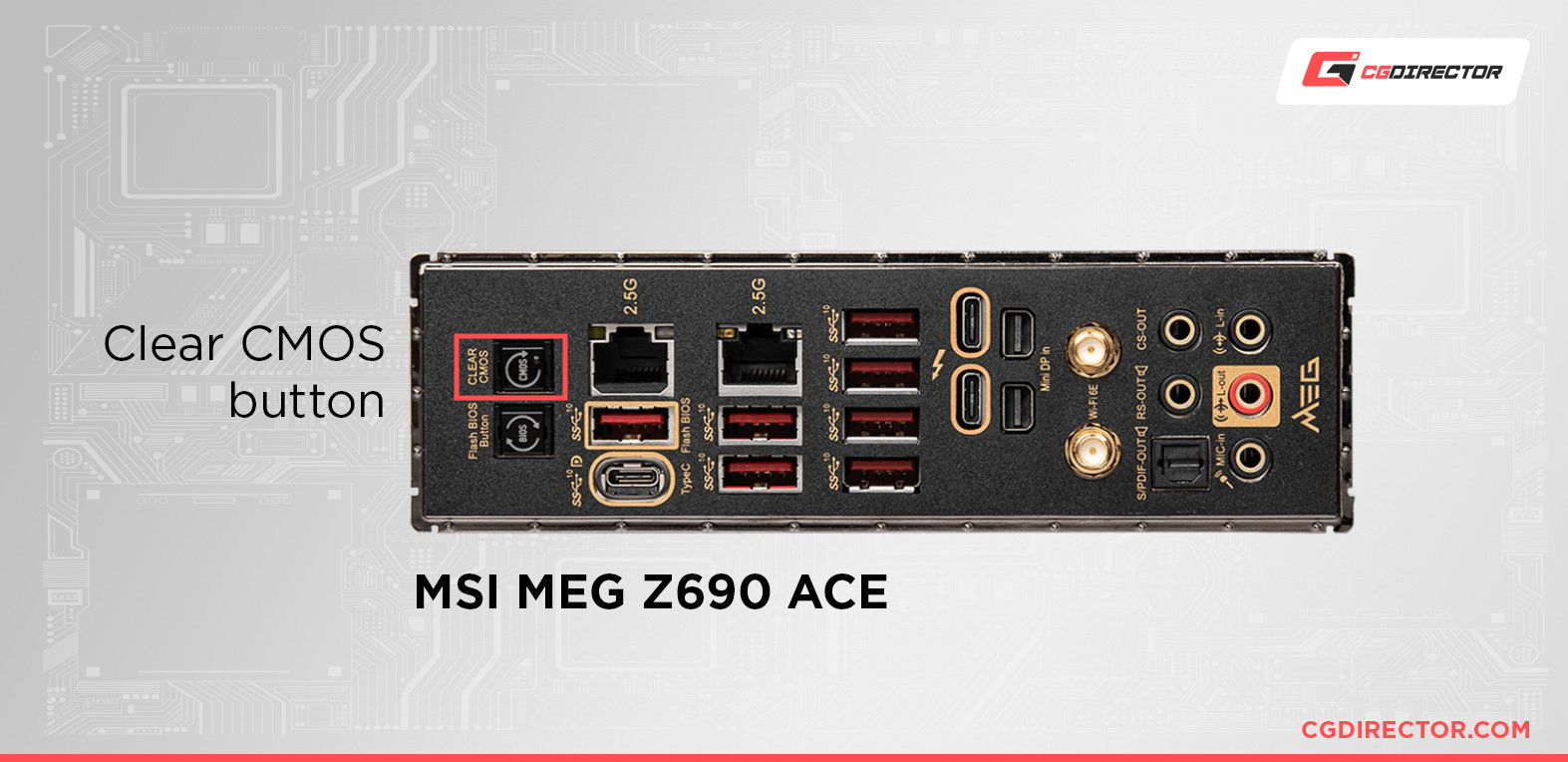
Source: MSI
To initiate it, turn your system on and press the CMOS/BIOS reset button and you should be good to go. Some Motherboards want you to trigger the Button when the System is off. Consult your Manual if you’re unsure which one it is.
Using the Jumper
Most boards don’t have physical buttons for clearing CMOS.
But, the same thing can be done with the CMOS jumper. We’re referring to two or three pins located near the CMOS battery.
You’ll see either JBAT1 or CLEAR_CMOS written next to it directly on the Motherboard.
The JBAT1, which usually has only two pins, will clear CMOS if you place a jumper on it to short the two pins. (Use any other jumper on the Motherboard) Short the pins for a minute and replace the jumper where you took it from. (if you took it from other pins on the motherboard)
The CLEAR_CMOS, which usually has 3 pins, can be set up in positions 1-2 and 2-3. The default is the (usually) already present jumper on pins 1-2. Set the jumper to pins 2-3 to clear CMOS and after a minute, move it back to 1-2.

Resetting from the BIOS Menu
People tend to clear CMOS when they can’t even get into BIOS/UEFI.
If you can access your BIOS, though, and you still want to reset the settings, simply select the “Reset BIOS to (Factory) Default” option and that’s it.
Why Would You Need to Clear CMOS?
Here are the three main reasons why you might need to clear CMOS:
Troubleshoot Hardware Compatibility Issues
Clearing CMOS won’t give your system or motherboard performance benefits.
However, it can help you in the process of troubleshooting by resetting the system settings. This will help you get to the bottom of the problem much easier, especially after installing new hardware into your machine.
After Unsuccessful Overclocking Attempts
Additionally, overclocking enthusiasts might be familiar with the best CMOS clearing methods as they are sometimes the only way back after unsuccessful overclocking attempts.
Resetting BIOS settings to default will get rid of overenthusiastic overclock setups.
There are motherboards that can detect malfunctioning overclocking setups and reset BIOS settings back to factory values without you needing to do any manual labor.
The perks of having high-end boards, eh?
Reset System-Level Password
Another reason for clearing CMOS is to reset a system-wide password, we can’t forget about that one.
If you’d to make changes to a PC that has a system-wide password, the easiest way to get rid of it is to clear its CMOS. You should be good to go in a matter of minutes.
Conclusion
Here’s how you can clear CMOS:
- Removing the CMOS battery is still the most common way of clearing CMOS / resetting BIOS
- CMOS chips don’t store BIOS data anymore. These are typically stored in Southbridge or Super I/O chips
- Clearing CMOS can be done in several ways, including removing the battery, using the jumper, or pressing the clear CMOS button
- Clearing CMOS can help you with troubleshooting, resetting system-wide passwords, and resetting BIOS defaults after unsuccessful overclocking or hardware upgrades.
FAQ
Does Resetting CMOS Delete BIOS?
No, it doesn’t delete the BIOS itself but rather just resets all options to their default values.
Clearing or resetting CMOS by removing the battery, using the CMOS jumper, or pushing the clear CMOS button on startup will delete your current BIOS settings and reset them to factory defaults.
How to Clear CMOS?
There are three main methods of clearing CMOS:
- Removing the CMOS battery and then plugging it back in after a couple of minutes.
- Moving the CMOS jumper to the secondary position, keeping it there for a few minutes then moving it back to the default position. You can use a screwdriver or another metal object too.
- Powering on the system then press the clear CMOS / BIOS button located on the motherboard or rear I/O panel.
Should I Clear CMOS Before Updating BIOS?
No, there is no need to clear CMOS before updating the BIOS.
The same goes for clearing CMOS after updating the BIOS, though we’ve seen people do it because it’s “good practice”.
Can I Clear CMOS While the PC is On?
No! To clear CMOS, you need to turn your computer off, disconnect it from the power source, and empty the capacitors by trying to power it on a couple of times.
After doing all of the above, you’re free to clear your CMOS by using one of the above-mentioned methods.
Over to You
What are your thoughts on all this?
Have you managed to fix the issues by clearing CMOS or are they still present?
If you’re still having trouble, hit us up in the comments below or our forum with whatever issues you have that could be fixed by tampering around with CMOS/BIOS.

![Where Do You Connect PC Fan PWM Cables To? [Beginner’s Guide] Where Do You Connect PC Fan PWM Cables To? [Beginner’s Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/12/Where-Do-PWM-Cables-Go-Beginners-Guide-Twitter-1-594x335.jpg)
![How To Connect Front Panel Cables To Your Motherboard [Guide] How To Connect Front Panel Cables To Your Motherboard [Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/01/How-To-Connect-Front-Panel-Cables-To-Your-Motherboard-Twitter-copy-1-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments