TABLE OF CONTENTS
In the matchup of Corsair RMX vs RM PSUs, which power supply series is best? What’s the actual difference between the two, anyway?
Today, I’ll answer these specific questions and help point you toward the right power supply for your needs.
Corsair RM and RMx PSUs are both pretty well-reviewed units, so either way, you should be fine once I’ve outlined the specifics.
What is a Corsair RM PSU?
Let’s start with explaining what a Corsair RM PSU is since it was actually released first. By a few years, in fact.
The Corsair RM PSU series launched as a replacement for Corsair TX Series Power Supplies in September of 2013. It included 80+ Gold Efficiency, Full Modularity, and Zero RPM fan modes across every model.

Zero RPM fan modes allow for a user’s power supply to operate in complete silence until a certain temperature threshold is passed.
This helps keep noise levels low, especially at idle, and (in theory) should result in longer life for the PSU fan. Granted, PSUs are generally built to last, and the RM Series boasts a clean 10 Year Warranty.
The main difference between the two series from the RM user’s perspective will most likely be the change in cabling.
Since the RM Series does not have capacitors in its cables, its cables are actually more flexible and easy to work with than the RMx PSU’s. That’s a minor spoiler for an upcoming section but felt appropriate to clarify here before explaining the RMx.
What is a Corsair RMx PSU?
The Corsair RMx PSU Series was released in late September of 2015, about two years down the line from Corsair RM Series’ original release. And as the minor change in naming scheme implies, these still are largely the same PSUs with the same features.
Corsair RMx PSUs also boast 80+ Gold Efficiency, Full Modularity, and a zero RPM fan mode across the board!

That’s…almost the same as the Corsair RM Series. Uncannily so, even. They even have the same 10 Year Warranties, at least as of initial writing in July 2022!
Truthfully, you’d be hard-pressed to tell the difference between the two by glancing at them side-by-side in your typical part picker or spreadsheet.
So let’s compare:
What’s The Difference Between Corsair RM and Corsair RMx PSUs?
So, what’s the difference? The first major difference starts on a more fundamental level: the capacitors inside the Corsair RMx PSUs. Compared to the RM Series PSUs, they’re composed of Japanese capacitors across-the-board.
Japanese capacitors are considered to be of higher quality and are tested more vigorously for heavy usage conditions, at least according to Corsair.
Additionally, the cables that come with an RMx PSU also have capacitors. This makes them a bit stiff for power supply cables, definitely stiffer than their RM cable counterparts. While this may also provide a boon to power delivery, in theory, cable management is also a fairly important part of any PC build.
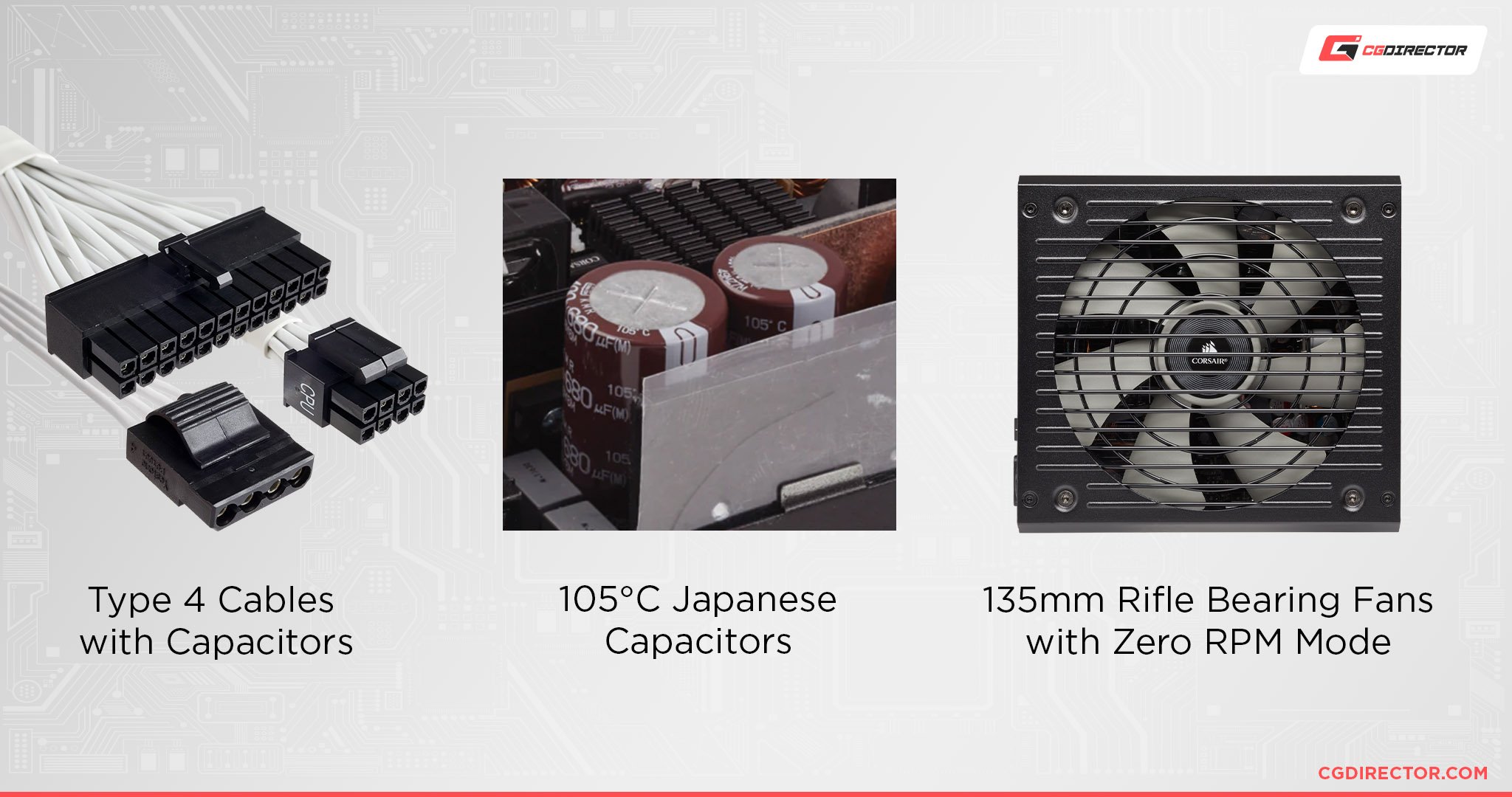
Finally, RMx PSUs also have slightly thicker MagLev bearing fans. These are also quieter due to their low-friction bearing.
Here’s an overview comparing Corsair’s RM and RMx PSUs directly:
| RM | RMx | |
|---|---|---|
| Zero RPM Fan Mode | Yes | Yes |
| Internal Capacitors | 105°C (Chinese) | 105°C (Japanese) |
| Efficiency Rating | 80 Plus Gold | 80 Plus Gold |
| In-Cable Capacitors | No | Yes |
| Modularity | Fully Modular | Fully Modular |
| Warranty | 10 Years | 10 Years |
| Fan Bearings | Regular Bearing | magnetic Levitation Bearing |
| Price (850W) | ~130$ | ~160$ |
When To Buy a Corsair RM PSU Instead
If you prefer a better out-of-box experience with minimal fuss and don’t see yourself pushing the power limits of your PSU, a Corsair RM PSU may be the better option.
Besides being cheaper, Corsair RM PSUs have more flexible cabling than Corsair RMx PSUs. This makes them ideal to be used right away in smaller Micro ATX and Mini ITX PC builds, which would naturally prove harder to work in with stiffer cabling.
If you don’t have specialized power or noise concerns, a Corsair RM PSU probably makes more sense.
When To Buy a Corsair RMx PSU Instead
If you don’t mind slightly stiffer cabling (easier to manage in a larger Micro ATX or proper ATX PC build) and paying a small price premium, definitely consider a Corsair RMx PSU!
When you move past the cabling downside, the fan runs quieter even under load while Silent RPM fan mode is no longer active. The price difference is rarely more than ten dollars, and it’s easily in favor of the RMx when the gap is that small.
Additionally, the Japanese capacitors add further reliability to the RMx PSUs.
While it’s true that they’re rated for the same lifespan as their non-X counterparts, clean and reliable power delivery is a treasured part of any overclocker’s build. Ensuring the highest quality of hardware in your budget at every step in the process can help facilitate that.
Are There Other Corsair PSU Series?

Image Source: Corsair
Yes, actually! On Corsair’s site, their PSU Series fall into one of four overall categories: iCue Smart PSUs, Efficiency & Electrical Performance PSUs, Modular & Quiet Performance PSUs, and Reliable & Continuous Power Delivery PSUs.
Oh, and the letters used to name a series definitely don’t mean anything.
I’ve searched and searched for actual days and found no evidence that RM or RMx have ever been short for actual words. If you’ve wondered what Corsair RMx stands for, now you know: the answer is nothing,
The Corsair RM and RMx Series both fall within the Modular, Quiet Performance PSU Category.
The only non-RM PSU that accompanies them is the Corsair SF600, which is an SFF (Small Form Factor) PSU.
The Corsair SF series is probably the only actual exception to the letters-don’t-mean-anything rule in their naming scheme.
The other categories include the following PSU series at the current time of writing:
- iCue Smart PSUs: Corsair CX Series, Corsair AX Series
- Efficiency & Electrical Performance PSUs: Corsair HX Series, Corsair SF Series
- Reliable & Continuous Power Delivery PSUs: Corsair CX Series, Corsair VS Series, Corsair CX-M Series
FAQ
What Makes a PC Suitable For Overclocking?
A PC’s suitability for overclocking is going to vary depending on a few different factors.
First, of course, you need a CPU and motherboard chipset that both support overclocking capabilities, to begin with.
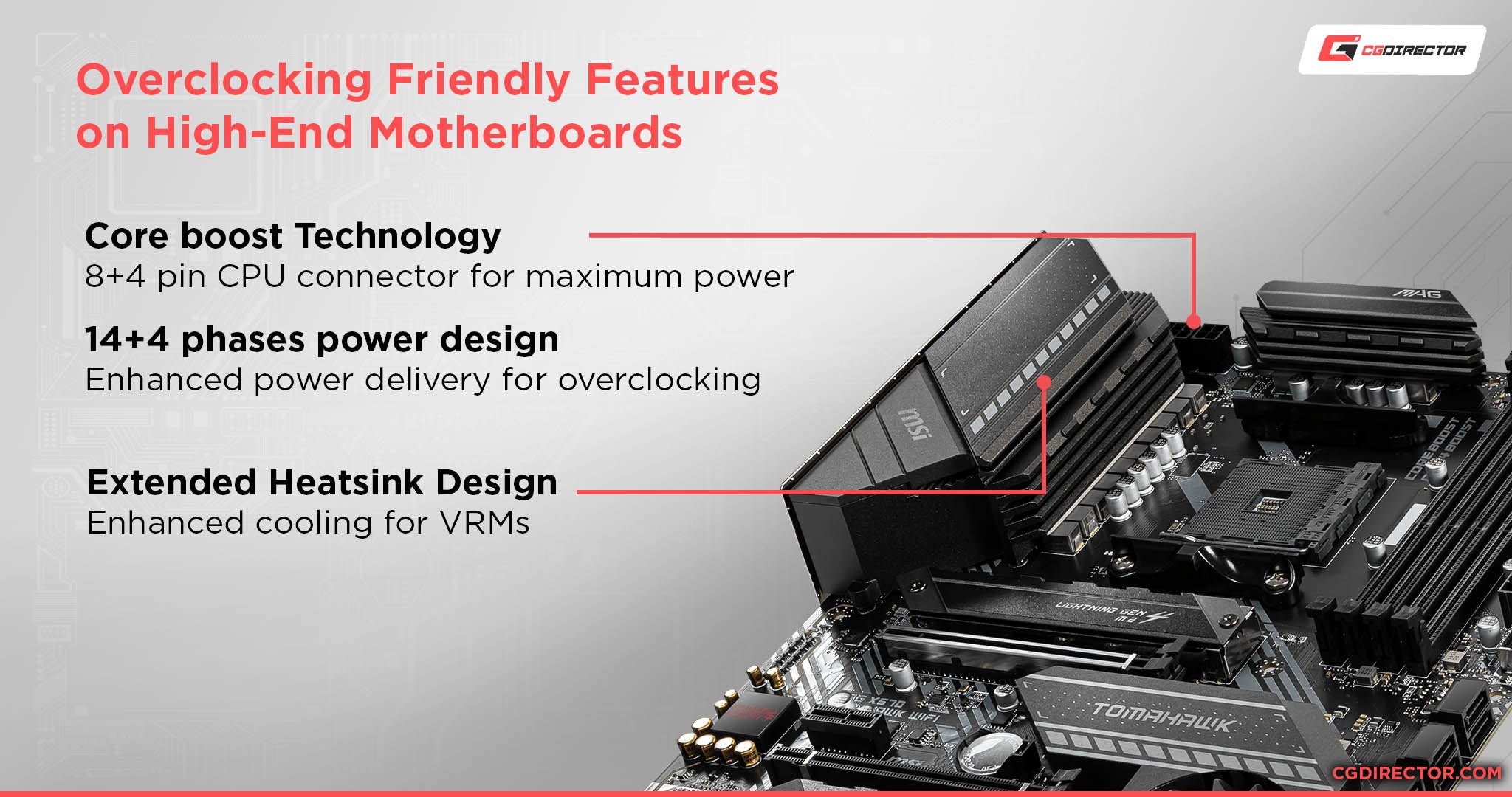
Source: MSI
Next, you’ll need high-quality motherboard VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) in order to achieve stable power delivery to the CPU. This will make it easier to push higher voltages and higher overclocks while maintaining system stability.
Finally, I actually do recommend a high-efficiency, high-quality power supply.
Both the RM Series PSUs should be good for overclocking, with the RMx PSUs being slightly better.
If you’re willing to spend more, however, you should also consider Corsair HX and Corsair AX Series Power Supplies.
What Are 80+ Power Efficiency Ratings?
A power supply’s 80+ Power Efficiency Rating is a rating of its total power efficiency (input voltage: output voltage and heat). High efficiency minimizes excess heat and power consumption.
80+ Power Efficiency levels are broadly divided into tiers, starting with basic 80+ Power Efficiency (~80%) and culminating in 80+ Titanium Power Efficiency (~92-94%).
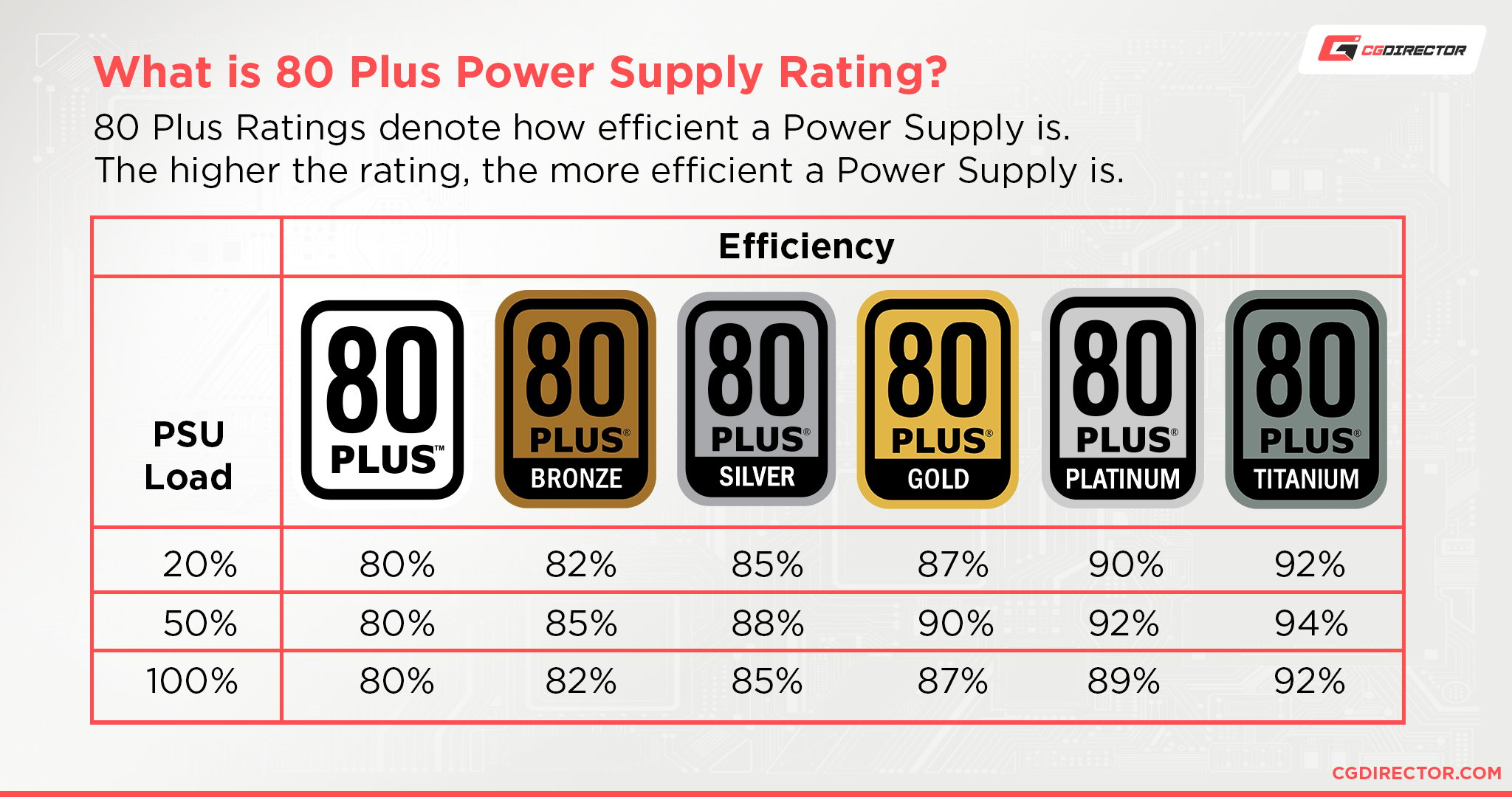
Both the Corsair RM and Corsair RMx PSU Series use the 80+ Gold Power Efficiency standard, which places them firmly in the mid-range of efficiency.
What Makes Modular Power Supplies Better?

Source: Seasonic
The Corsair RM and Corsair RMx PSU Series are both Fully-Modular Power Supplies.
This means you have the maximum amount of cable-related flexibility with these PSUs, including the ability to replace all PSU cables entirely with your own custom cabling for color theming, shorter/longer length, or really just about anything else.
Most of the practical benefits of Fully-Modular PSUs can be seen in Semi-Modular PSUs as well since Semi-Modular still allows most cables to be removed and only mandates the mandatory power cables being run at all times.
Non-Modular PSUs run all cables at all times, even if they aren’t in use, making Non-Modular PSUs by far the worst for cable management.
Over to You
And that’s it, for now! I hope that this article helped teach you more about Corsair Power Supplies, and Power Supplies in general for that matter.
Leave a comment below and let me know if you have any more PSU questions, or head to the Forums to ask our wider community for tips!
Until then or until next time, happy building! And don’t forget to get a Power Supply with a healthy range of wattage above your maximum estimated usage to ensure efficiency and stability.
![Corsair RM vs RMx PSU’s [Differences And The Better Pick] Corsair RM vs RMx PSU’s [Differences And The Better Pick]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2022/08/Corsair-RMX-vs-RM-PSUs-Whats-The-Difference-Which-Should-You-Get-Twitter.jpg)

![Best Low-Profile & Compact Graphics Cards (GPU) for your needs [2024 Guide] Best Low-Profile & Compact Graphics Cards (GPU) for your needs [2024 Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2021/04/Best-Low-Profile-GPUs-Twitter_1200x675-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments