Ever asked yourself ‘what’s the difference between RAM and ROM’? If you’ve seen both acronyms in action, it’s a natural question to ask, especially if you can deduce that both of those “M”s mean “Memory”.
Let’s take a moment to talk about PC memory, then break down all you need to know about the difference between RAM and ROM!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A Brief on Memory in PC Hardware
Before we sink our teeth into the main question, I want to take just a moment to talk about “memory” and how that word is used in PC hardware.
First, all forms of “memory” fall into “volatile”, “semi-volatile”, and “non-volatile” categories.
These all refer to whether or not power is needed for that memory to store information, with volatile referring to memory that only works when powered and non-volatile referring to memory that keeps information even when powered off.
What’s The Difference Between RAM and ROM?
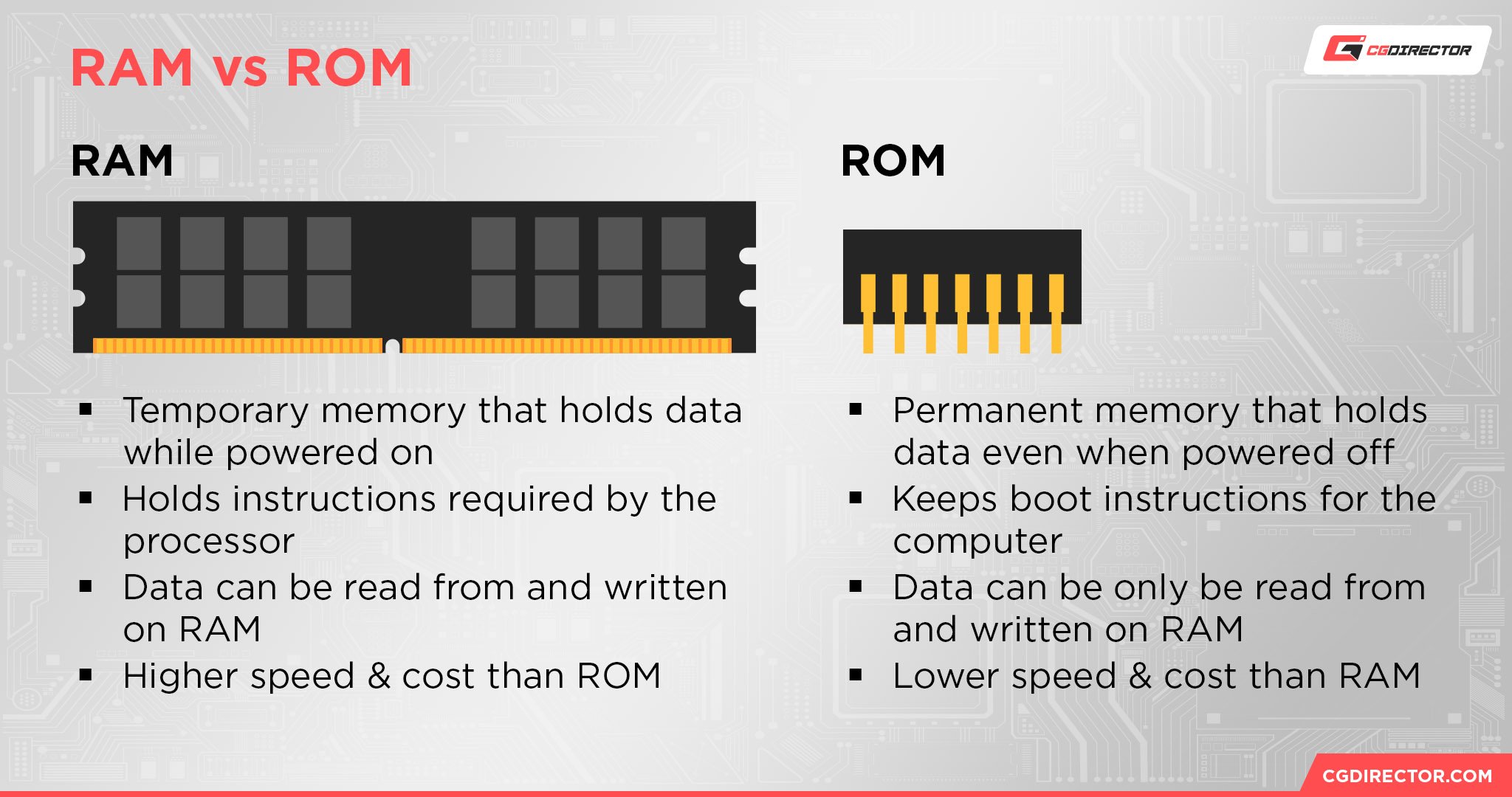
RAM stands for Random Access Memory, and refers to the volatile memory inside of your PC that is used for managing real-time tasks.
RAM is naturally cleared whenever your PC is powered off, and does not store any system information between PC restarts. It will be written to and read from nonstop as long as your PC is in active use.
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory, and refers to non-volatile memory used by a variety of components.
Non-volatile memory keeps its information when powered off, and that “Read-Only” means exactly what you think it does: ROM memory cannot be written to, only read from.
So, that’s the difference— and it’s a pretty major one, too. RAM’s utility in your PC likely needs less explanation, since it’s generally understood that more RAM is better.
No one has ever said “more ROM is better”, though, so we should spend some time in the follow-up sections elaborating on how ROM memory is actually used in PC hardware.
FAQ
What Devices Use ROM Chips?
A wide variety of devices use ROM chips, including (most likely) the one you’re reading this article on right now.
For example, a known method of resetting a motherboard’s BIOS is by removing the CMOS battery. This clears all existing settings and uses the motherboard’s existing ROM chip to restore the original BIOS settings.
Even RAM uses ROM! Specifically, XMP profiles and the such are kept on small ROM chips built into your RAM that provide its XMP information to your motherboard.
What Are ROM Files?
“ROM files” typically refer to backup copies of retro video games, and are also called “ROMs”.
Technically the same meaning applies here, but “ROM files” in a gaming context refers to a cartridge game’s extracted data.
Sometimes they come in a .rom file, but other file containers can be common, too. Newer disc-based game backups are also called ROMs sometimes, though technically these are usually ISOs (disc images).
Is ROM Better Than RAM?
As popular as this question is, it’s hard to give it a straight answer because ROM and RAM are simply made for completely different tasks.
ROM is not better than RAM in any way that impacts the user experience, though, since RAM is integral to there being a user experience to enjoy at all.
ROM is in frequent use but works best when you simply aren’t aware of its presence at all since you can’t actually do anything to modify it.
Over to You
And that’s all!
I hope this article helped clarify the difference between RAM and ROM for you.
As it turns out, RAM isn’t the only kind of memory that exists in PC hardware, and somehow not even the only kind of memory used on a RAM stick. Hardware is funny like that, sometimes.
Any other questions about RAM, ROM, or PC hardware? Please ask them in the comments below, as I’ll be happy to help you.
Alternatively, you can try your hand with long-form discussions in the CGDirector Forum, where you can interact with the rest of the Team and our Community of Experts and Enthusiasts.
Until then or until next time, happy computing!



![How Much RAM Does my PC Support? [How to Check] How Much RAM Does my PC Support? [How to Check]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/10/How-Much-RAM-Can-My-Computer-Take-Twitter-594x335.jpg)


0 Comments