TABLE OF CONTENTS
Random Access Memory (RAM) varies dramatically in performance, from one generation to the next; and this is particularly the case between GDDR5 and GDDR6.
But with each upgrade the increase is not just in performance, but also in price. So, the question becomes:
Is the extra cost associated with components that harbor high-end memory modules – like the most recent GDDR6X – really worth it?
Reaching the end of the GDDR6 generation of VRAM (Video RAM), let’s compare the two memory generations and list the differences between the two.
This way, we can get a better understanding of their current purpose and use, while also getting an idea of what we can expect when newer generations of SDRAM begin to appear.
What Does GDDR Stand For?
In short, GDDR stands for Graphics Double Data Rate. This is a type of SDRAM or SGRAM, which stands for Synchronous Dynamic/Graphics Random Access Memory.
Where is GDDR Memory Used?
As denoted by its name, GDDR memory is used in graphics cards and is utilized in everything from 3D modeling, video editing, graphic design, compositing, and even gaming.
Any type of RAM, be it System RAM or Video RAM, is used to cache Data that is needed by either the CPU or GPU for processing.
You can think of RAM as a very fast storage device – with the downside of volatility, meaning without power, all data is lost.
For 3D Rendering, the VRAM will hold scene Data that can then be accessed by the Render Engine.
In Gaming, as well, the VRAM will hold scene Data, such as animations, textures, meshes, lights and other objects, that the GPU needs to display the current state of the Game-Environment and Characters.
Typical Graphics Cards with GDDR Memory
What are some popular examples of GPUs that use either GDDR5 and GDDR6 SDRAM? Let’s take a look.
Graphics Cards with GDDR5 Memory
NVIDIA
- GeForce GTX 980 Ti
- GeForce GTX 1070 [Ti]
- GTX Titan
- GeForce GTX 1080 [Ti] (GDDR5X)
- Titan X Pascal (GDDR5X)
AMD
- Radeon HD 7990
- Radeon RX 480
- Radeon RX 580
- Radeon RX 590
- Radeon R9 295X2
Graphics Cards with GDDR6 Memory
NVIDIA
- GeForce RTX 2080 [Ti]
- Titan RTX
- GeForce RTX 3060 [Ti]
- GeForce RTX 3080 [Ti] (GDDR6X)
- GeForce RTX 3090 (GDDR6X)
AMD
- Radeon RX 5600 XT
- Radeon RX 5700 [XT]
- Radeon RX 6700 [XT]
- Radeon RX 6800 XT
- Radeon RX 6900 XT
GDDR5 vs GDDR6 Compared – What’s the Difference?
The leap from generation to generation usually has an intermediary step, which is denoted by an “X” suffix.
Therefore, before we get into the difference between GDDR5 and GDDR6, let’s also see what upgrades were provided to GDDR5 for enthusiast-level graphics cards.
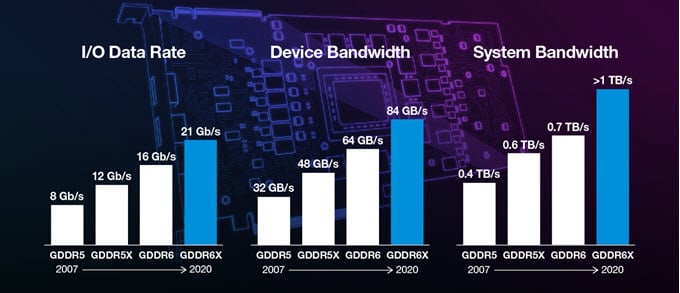
Image-Credit: graphicscardhub.com
GDDR5 to GDDR5X
Even for half-generational leaps in memory, we get significant upgrades in performance.
When GDDR5 was succeeded by GDDR5X, we saw a theoretical 50% increase in per pin data rates (increasing from 8 Gb/s to 12 Gb/s), device bandwidth (increasing from 32 GB/s to 48 GB/s), and system bandwidth (increasing from 400 GB/s to 600 GB/s).
In addition, we also have a decrease in required voltage, from 1.5 V to 1.35 V.
The only issue found with GDDR5X is that it was expensive and only found in Nvidia’s higher-end GPUs.
GDDR5(X) to GDDR6
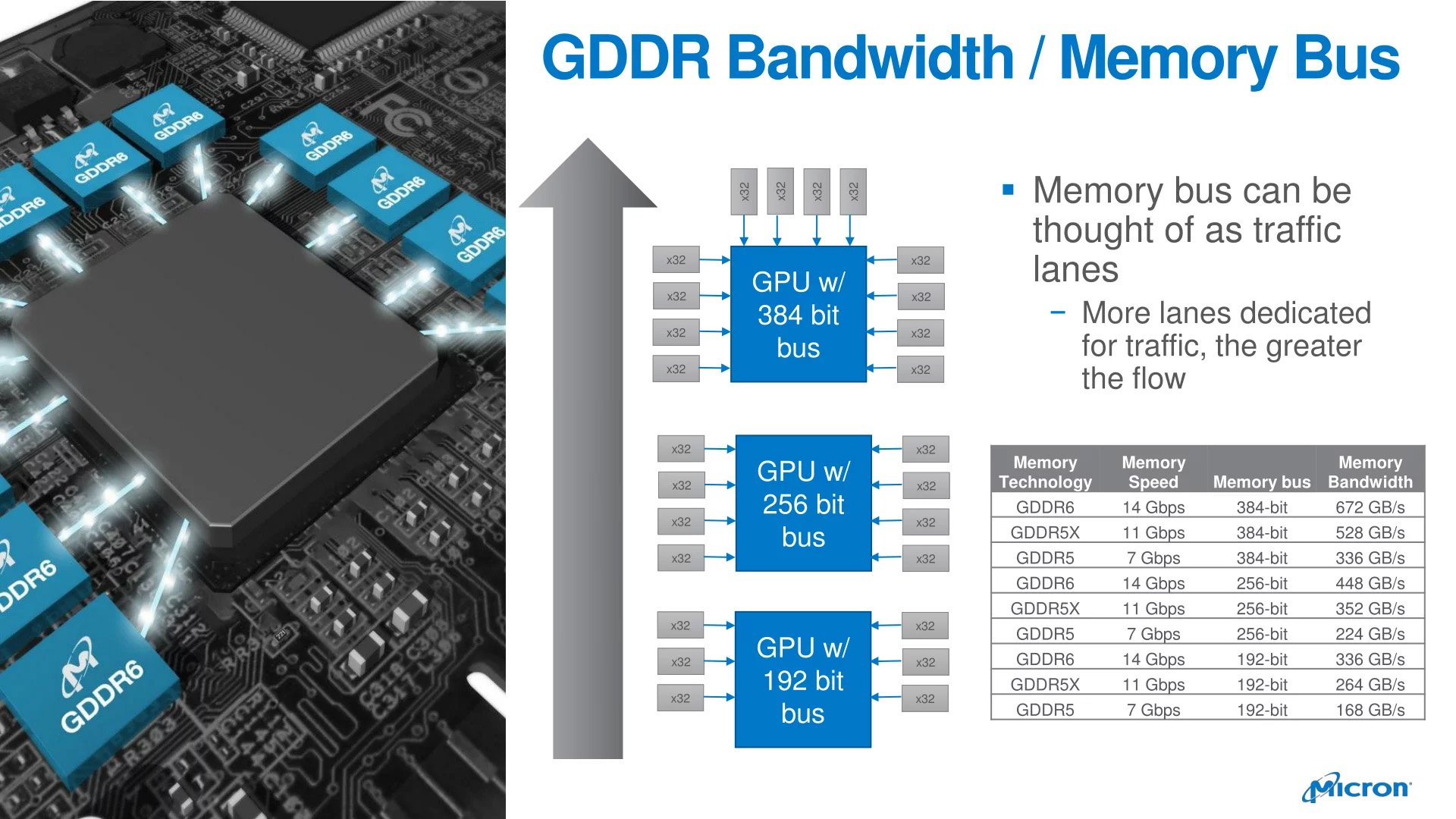
Moving up to GDDR6, we see an equivalent increase of performance that has it surpass GDDR5 by a 100% margin, and GDDR5X by a 50% margin in most performance metrics.
Per-pin data rates were increased to 16 Gb/s, and its bandwidth increased to 64 GB/s.
The system bandwidth saw a smaller upgrade, increasing from 600 GB/s to 700 GB/s. The power consumption was also decreased, from 1.35 V to 1.25V.
Another important upgrade found between GDDR5(X) and GDDR6 is in the prefetch memory architecture; as the memory arrays are separated into two channels, instead of one.
These two fully independent channels have a read or write memory access of 256 bits (32 bytes wide).
This access granularity (amount of data read or written by a single read/write command) configuration allows for double the burst length of GDDR5, per channel.
GDDR6 to GDDR6X
Though once again only utilized by the most expensive Nvidia GeForce GPU models, GDDR6X is a significant performance upgrade to GDDR6. It has a 21 Gb/s per pin data rate, an 84 GB/s device bandwidth, and a 1 TB/s system bandwidth – an increase of almost 43% in comparison to GDDR6.
This drastic increase in system bandwidth was made possible using a new signal transmission technology – named PAM4 – by Micron; providing multi-level signaling.
Power consumption also marginally dropped by about 3% in power per bit transferred.
How Much Faster is GDDR6 Over GDDR5 on Average?
We’ve seen the theoretical difference in performance between the two generations of GDDR SGRAM, but how do they compare in real-world benchmarks?
If all other external factors are equal, does the memory itself actually provide a tangible increase in performance?
Well, there is one way to test the intergenerational impact of these memory modules, and that is the Nvidia GeForce GTX 1650. Why is this GPU perfect for the task?
Nvidia released two iterations of the same GPU: one with GDDR5 VRAM, and one with GDDR6. They have almost identical specifications, with a few exceptions.
Specifications
The GDDR5 version has higher base (1485 MHz vs 1410 MHz) and higher boost (1665 MHz vs 1590 MHz) clock speeds.
On the other hand the GDDR6 version has a higher effective memory clock speed (12,000 MHz vs 8,000 MHz), and a higher memory bandwidth (192 GB/s vs 128 GB/s), despite having the same memory bus width of 128 bits.
Performance Benchmarks
According to benchmarks featured by VideoCardz, the GDDR6 Nvidia GeForce GTX 1650 displayed a performance boost between 5% and 8% for multi-purpose synthetic tests.
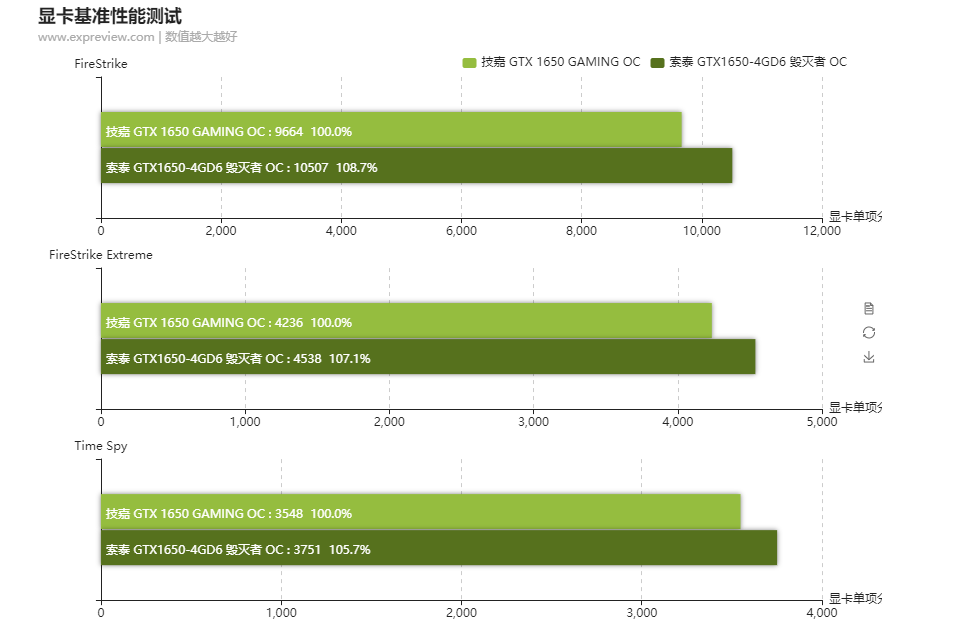
It also displayed a varied boost in gaming performance, ranging between 2% and 10% (depending on the game); which averages out to about 6%.
Additionally, despite both GPUs having the same Thermal Design Power (TDP) of 75 watts, the GDDR6 model used ~9% less power than the GDDR5 version.
FAQs
Now that we have a general idea of what differentiates GDDR5 and GDDR6 memory types, let’s take a look at some of the most common questions related to the topic.
Is 4 GB GDDR6 Better Than 8 GB GDDR5?
The answer to this question depends on whether or not the VRAM has the same memory bus. If they do, then the GDDR6 will offer double the memory speed and bandwidth of the GDDR5 VRAM.
Additionally, GDDR6 consumes less power, and draws 13% less Voltage than its predecessor, allowing the surplus in energy to be used by the GPU itself.
Therefore, if the memory bus is equal in size, GDDR6 4 GB of GDDR6 is better than 8 GB GDDR5, but to a marginally noticeable extent.
Of course, only in terms of performance! If you need more than 4GB of VRAM for your type of workloads, you’ll likely see a higher performance with a larger VRAM pool into which your workload fits entirely, even if it is slightly slower.
Can I Replace GDDR5 with GDDR6?
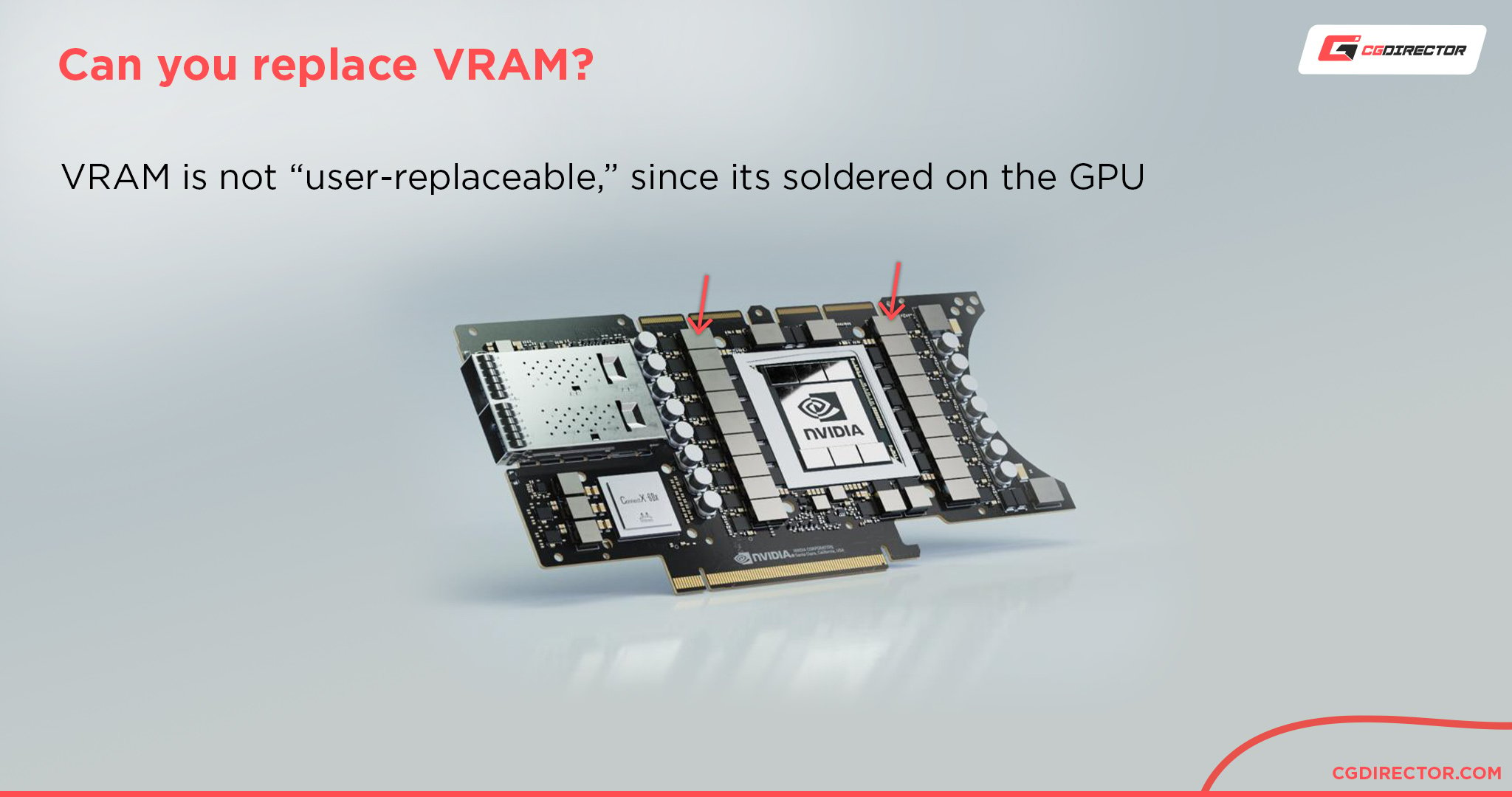
Unfortunately VRAM is not replaceable the same way DRAM is, so it’s not like a set of memory sticks that you can add and remove according to your needs.
That being said, it is technically possible to change the memory chips of a GPU, but you would need a specialist with a BGA rework station and knows exactly how to carry out the process.
Contrary to a PC’s regular System DRAM, GDDR VRAM is soldered onto the GPU’s PCB.
Is the GTX 1650 GDDR5 or GDDR6?
Funny enough, the answer to this question is: yes. The Nvidia’s GeForce GTX 1650 has two distinct versions which are named G5 and G6. The G5 has GDDR5 VRAM, while the G6 has GDDR6.
Is 8 GB of GDDR6 Enough?
This will depend on your intended use. For most 1080p gaming applications, 8 GB of either GDDR5 or GDDR6 VRAM is more than enough. However, for doing professional work, such as 3D GPU Rendering, High-Poly Sculpting, or 4K Video Editing, you’ll see fewer slowdowns with more than 8GB of RAM.
If you’re wondering what memory capacity you need for your specific workload, make sure to check out our article written for this exact topic.
Why Is There a GDDR6 Shortage?
There, indeed, has been a shortage of GDDR6 as of late (2020-2021), which has limited the supply rate for both Nvidia RTX 30 Series and Radeon RX 6000 Series GPUs.
There are several reasons why we may be experiencing this shortage.
Firstly, almost all current-generation GPUs use GDDR6; with the exception of some high-end Nvidia GeForce RTX 30 Series GPUs.
This also includes the two latest gaming consoles: the Playstation 5 and the Xbox Series X/S.
Other factors include: the global semiconductor shortage and the fact that shipping priority has been allocated for medical supplies. GDDR6X memory is not as scarce as GDDR6, but, once again, it is only used in select Nvidia GeForce RTX 30 Series models.
Do You Need a New Motherboard for GDDR6?
Unlike DRAM, the motherboard is not dependent on the generation of GPU memory found in your graphics card. This means that if your Motherboard already runs a GPU with GDDR5 Memory, it will support a GeForce GTX 1650 (or other GPU) with GDDR6 video memory.
Conclusion
With each passing generational advancement in VRAM, we see a significant boost in performance; and this was definitely the case in the upgrade between GDDR5 and GDDR6.
However, there are some signs of diminishing returns that are beginning to appear in certain aspects of their performance.
Can we expect these diminishing returns to be exacerbated as VRAM technology progresses or will new and exciting innovations perpetuate the trend of a 50% to 100% increment in effective data rates?
Over to you
What’s your opinion on the matter? Let us know in the comments below! Also, if you have any questions on what GPU (and its accompanying VRAM) to choose from, make sure to leave a post in our expert forum.

![Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step] Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/04/Guide-to-Undervolting-your-GPU-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

![Are Intel ARC GPUs Any Good? [2024 Update] Are Intel ARC GPUs Any Good? [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/02/Are-Intel-ARC-GPUs-Any-Good-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

6 Comments
12 August, 2023
really appreciate it, I’m gonna buy now my laptop according to your article about GDDR6 4 GB Nvidia Geforce RTX 3050, I hope it works incredibly smoothly than the previous one, thanks again.
5 September, 2023
it does
21 July, 2023
Thanks
25 June, 2023
The 6600 and 6600XT cards have gddr6. RX6000 series wasn’t on the list above.
25 July, 2022
The article lists data speeds with the incorrect metric of GB/s instead of Gbps. One is Gigabytes, and the other is Gigabits. It’s a very important distinction.
8 August, 2022
Hey JT,
You’re right, missed that, thanks! Updated.
Cheers,
Alex