Ever wanted to know the difference between Graphics Card TDP vs TGP? You’ve come to the right place.
Today, I’ll be breaking down the difference between these two GPU terms, and clarify a few related questions as well.
Let’s get into it!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Graphics Card TDP vs TGP: What Does It Mean?
What Is Graphics Card TDP?
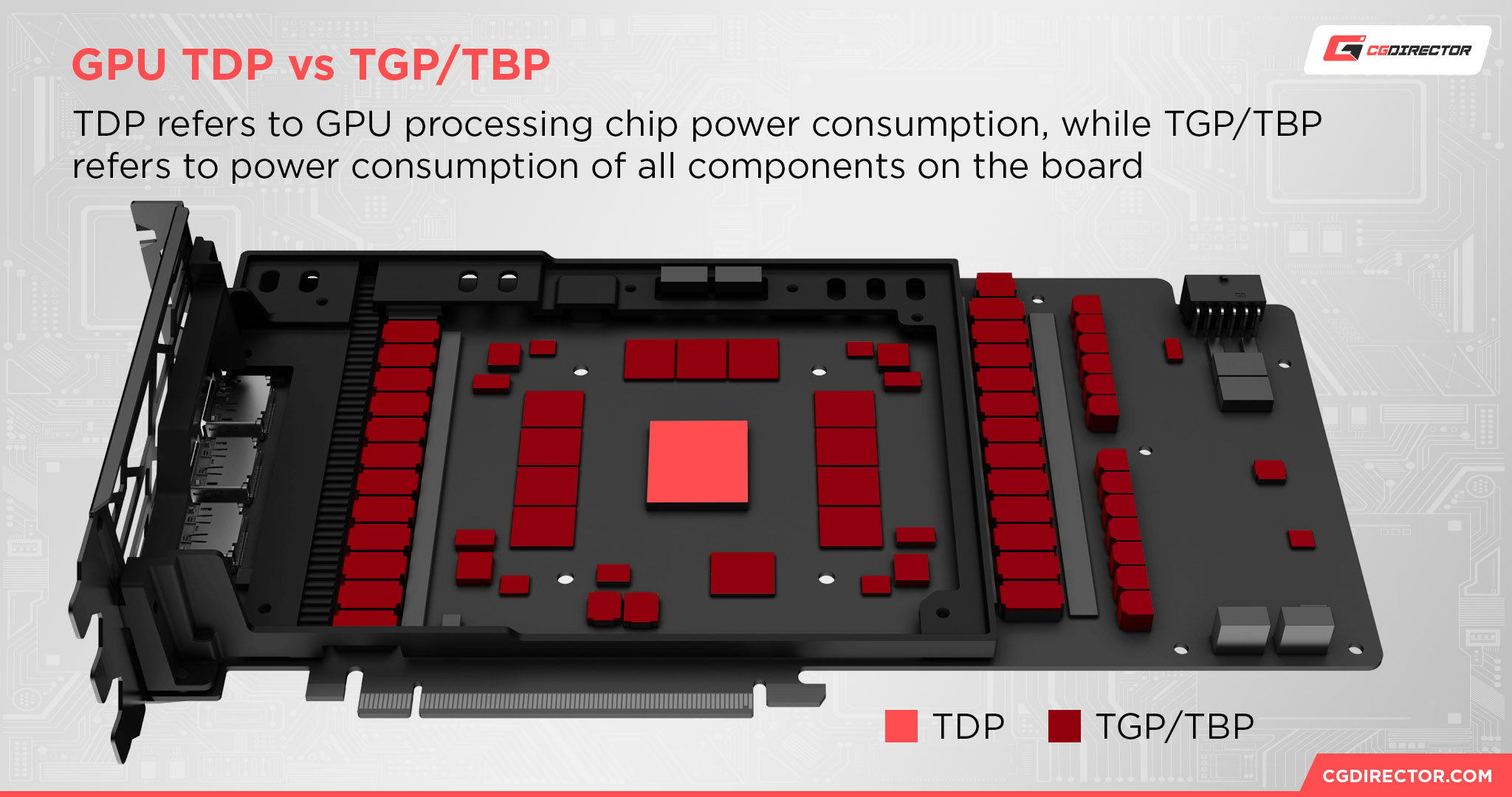
Graphics Card TDP refers to Thermal Design Power.
Thermal Design Power refers to the maximum intended wattage and heating of a given component. In the case of graphics cards, though, only the actual GPU processing chip is counted within TDP.
This means that the other components on a graphics card aren’t usually counted within TDP!
What Is Graphics Card TGP?
Graphics Card TGP refers to Total Graphics Power, a metric used by Nvidia to measure the entire graphics card’s power utilization, not just the GPU by itself.
AMD also has a similar metric called graphics card TBP, or Total Board Power, but the concepts are the same.
TGP and TBP include GPU TDP numbers but also include numbers needed for powering the fans and the rest of the graphics card, usually dedicated to cooling and occasional lighting features.
FAQ
Is Higher TDP Better or Worse?
Higher GPU TDP can correspond to higher performance (from the same/newer GPU architectures) but also corresponds to higher heat output and, thus, increased cooling needs.
And of course, GPU TDP can even encourage a higher grade of Power Supply if its demands are high enough, which is becoming common with dual 8-Pin GPU designs.
What Is Graphics Card MPC?
Graphics Card MPC refers to Max Power Consumption.
This is most similar to TGP and TBP but refers to a GPU’s maximum power consumption in any condition, including overclocking. This metric isn’t used nearly as often as the others listed in this article, but might still pop up in some product documentation.
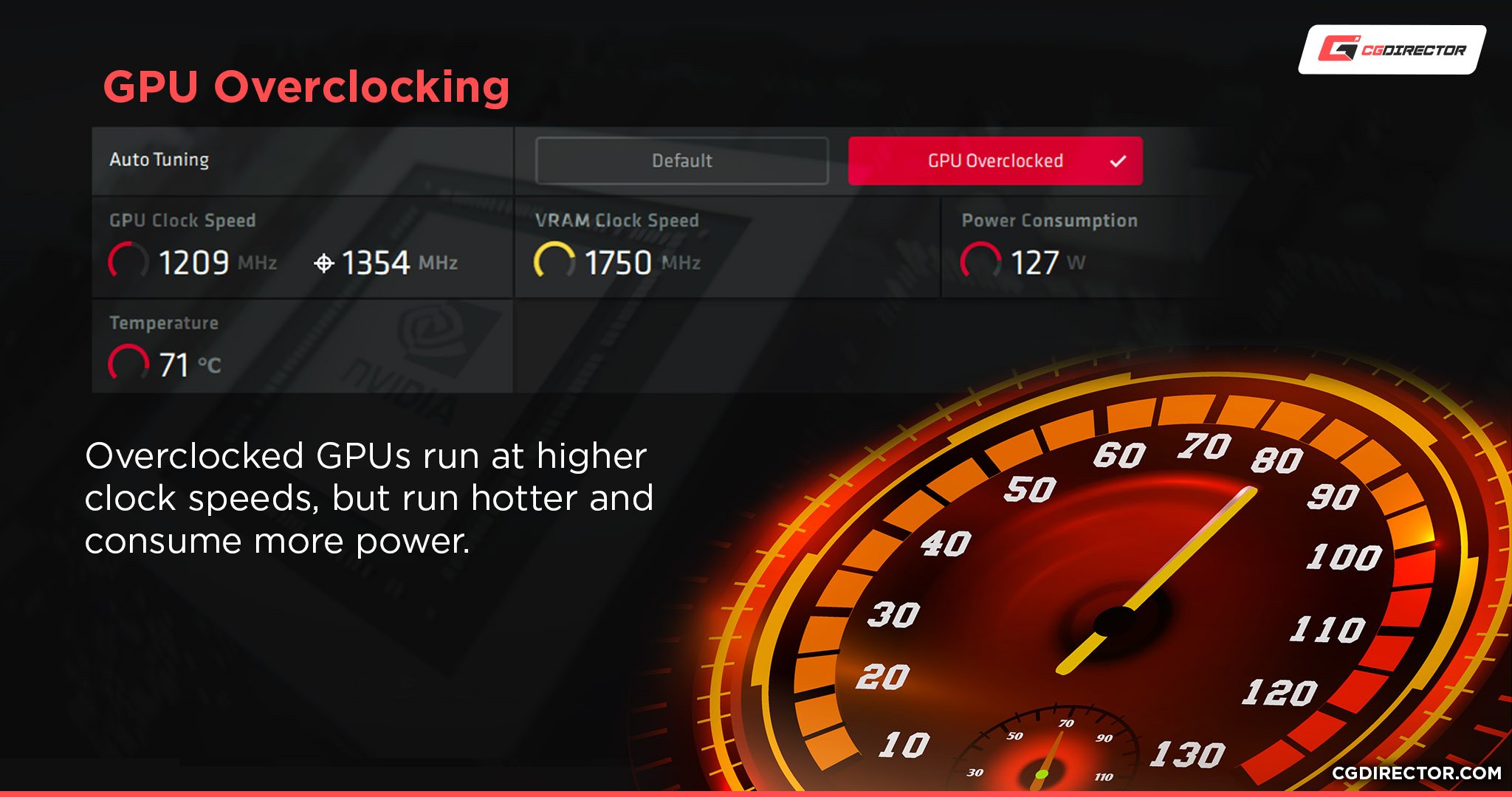
Does Overclocking Increase TDP?
Yes. Part of overclocking involves increasing voltage to your CPU or GPU.
In either case, doing so will increase both power and heat needing to be dissipated from the chip, resulting in a higher effective TDP.
This means overclockers should be particularly cautious to get high-quality power supplies with plenty of headroom and keep their components as cool as possible.
Over to You
And that’s all!
Despite their importance, TDP and TGP don’t actually require all that much explanation. These are just specs that naturally increase as you spend more on larger, more powerful graphics cards.
But do you have any other questions about PC hardware, power delivery, or cooling? Feel free to ask them in the comments section below, where me or another member of the CGDirector Team will be happy to help you.
You can also try our Forum for extended tech discussions with other Experts and Enthusiasts. Until then or until next time, happy computing!

![Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step] Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/04/Guide-to-Undervolting-your-GPU-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Is PNY a Good GPU Brand? [Updated] Is PNY a Good GPU Brand? [Updated]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/12/Is-PNY-a-Good-GPU-Brand-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Does Temperature Impact My GPU’s Performance? [Absolutely!] Does Temperature Impact My GPU’s Performance? [Absolutely!]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/09/Does-Temperature-Impact-My-GPU-Performance-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![How To Adjust Your GPU’s Fan Speeds [Step-By-Step] How To Adjust Your GPU’s Fan Speeds [Step-By-Step]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/07/How-to-adjust-your-GPUs-Fan-Speeds-to-prevent-it-from-overheating-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments