TABLE OF CONTENTS
Getting the most out of your PC hardware is paramount, and this is especially the case when it comes to Nvidia’s RTX – or ray tracing – functionality.
With but a few steps, anyone with the necessary hardware can utilize this groundbreaking technology with their setup.
In this article, we will provide you with all the relevant information on what ray tracing is exactly; and, subsequently, the RTX prefix found in Nvidia’s new GPU lineup. We will also list the steps necessary to take advantage of the ray-tracing rendering technique.
Nvidia’s AI-powered RTX applications – like their rendering solutions and RTX Voice – will also be covered.
For AMD GPU owners, worry not, as we will also go through the basics for AMD’s new ray-tracing Radeon RX 6000 series lineup.
What Is RTX, or Ray Tracing, and How Is It Utilized?
Put simply, ray tracing refers to a rendering process in which the color of pixels is calculated based on the pathways of simulated light; and its interaction with virtual objects.
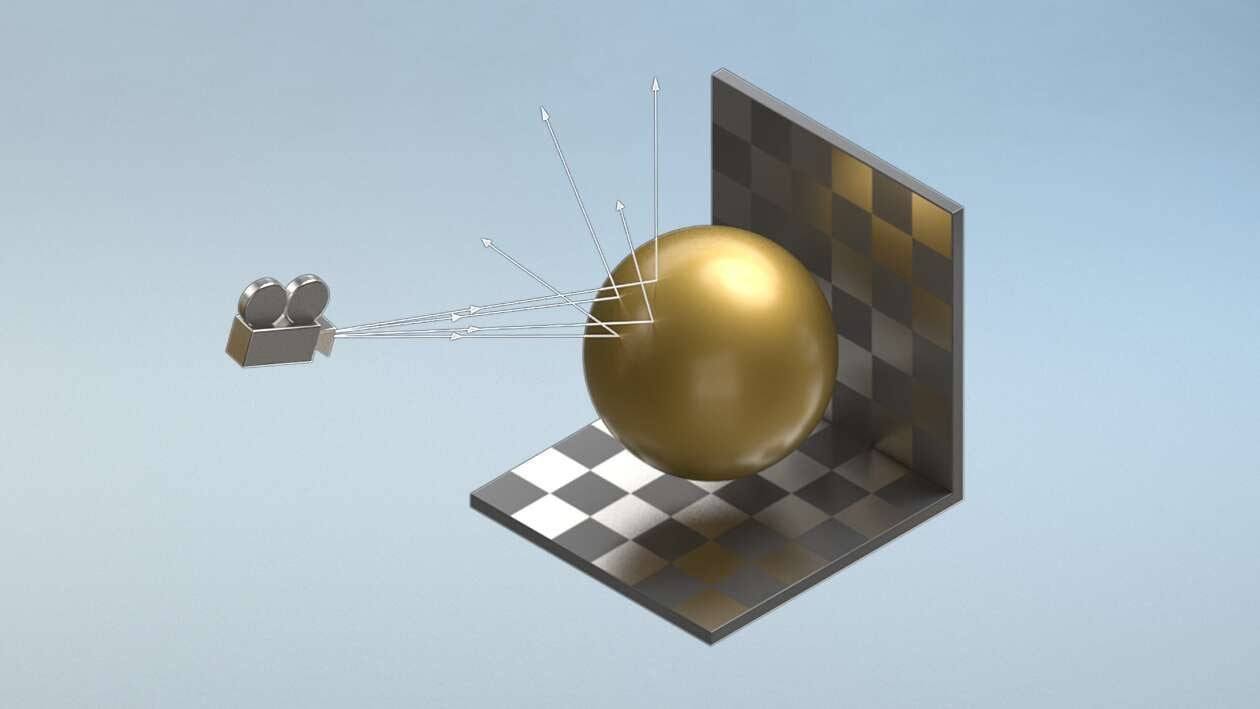
Image showing how rays move through a scene – Image-Credit: Nvidia
This process results in a high level of photorealism which can then be used for a wide array of applications that deal with visual imagery.
Applications ranging from a film’s VFX, over accelerating Offline 3D Rendering Engines to real-time graphical lighting-representation in video games.
The same array of visual outputs associated with light rays – like scattering, reflection, and dispersion – can also be used for acoustic effects; creating a more immersive audio environment.
Ray tracing has long been used for applications in which a longer rendering time is permissible, but it has only recently begun to see widespread use for concurrent rendering applications.
Both commercial GPU manufacturers – AMD and Nvidia – have adopted real-time ray tracing support; each in their own style and capacity.
Nvidia & RTX
Ray tracing was first introduced with Nvidia’s Turing architecture in their GeForce RTX 20-series GPUs.
This technology was later utilized – and improved upon – with Nvidia’s new-generation Ampere architecture and their GeForce RTX 30-series graphics cards.
Their new, 2nd generation RT (Ray Tracing) cores are now able to deliver twice the throughput of what their predecessors could muster.
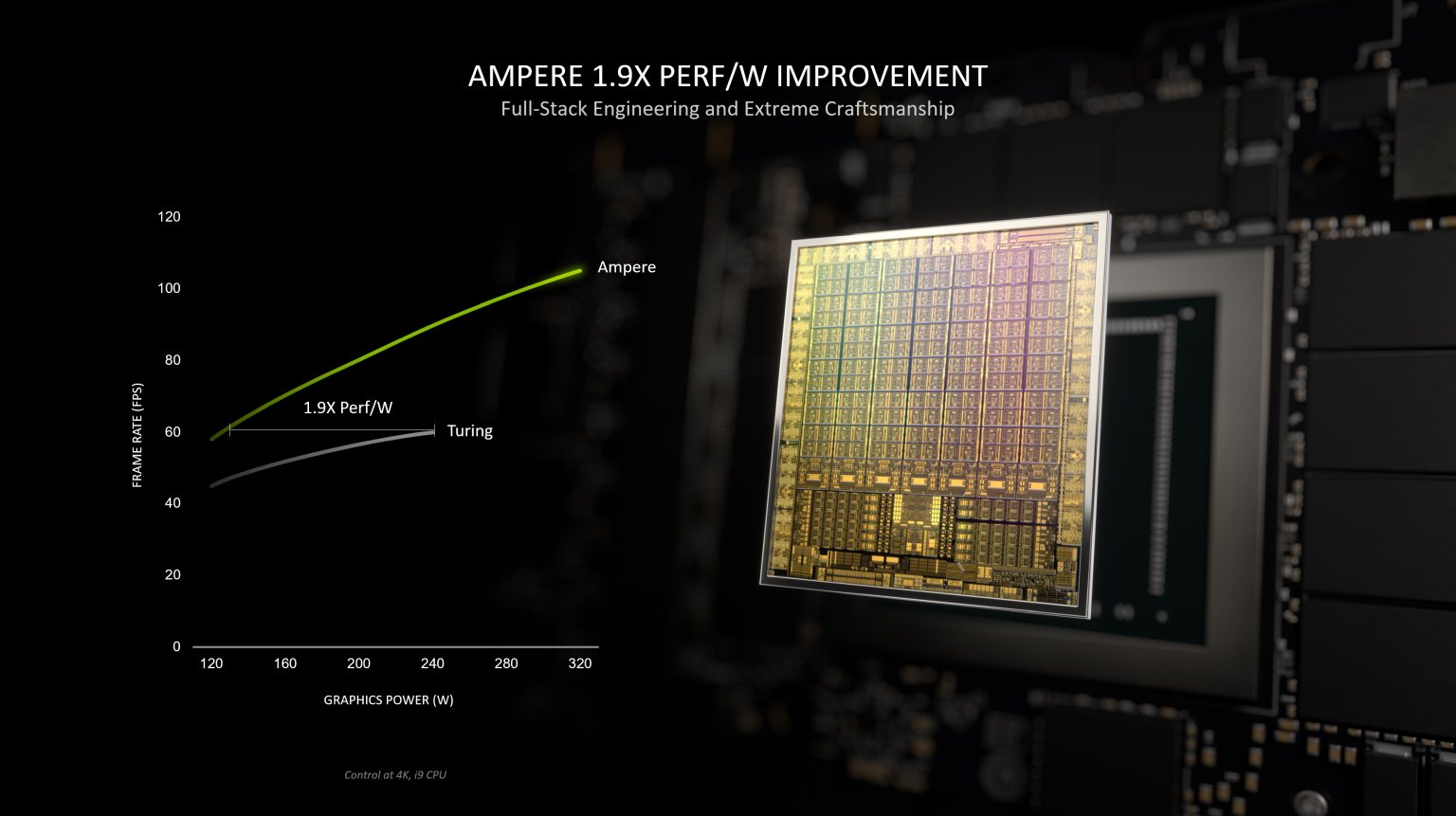
This Graph shows the performance uplift in 2nd Gen. RT Cores
RT cores are dedicated hardware components meant to hasten the ray tracing process by adding a dedicated pipeline (ASIC) to Nvidia’s Streaming Multiprocessors (SM).
AMD
In place of Nvidia’s RT cores, AMD GPUs utilize Ray Accelerators for their current-generation Radeon RX 6000 series processors.
These Ray Accelerators are built into the Compute Units (CU) of the graphical processor, effectively boosting their efficacy by alleviating some of the ray-tracing workload.
For a full rundown on RT Cores, Ray Accelerators, and more, make sure to check out our detailed article about everything related to GPU cores.
Performance Handicap
Real-time ray tracing does come at a cost. The process of simulating light-rays as they scatter throughout a virtual scene is quite strenuous on a GPU.
This demand translates into a decrease in overall graphical performance; especially with regard to framerates.
Since this concurrent rendering technique is new for AMD’s GPU architecture, the resulting performance is not quite as impressive yet as what Nvidia has to offer.
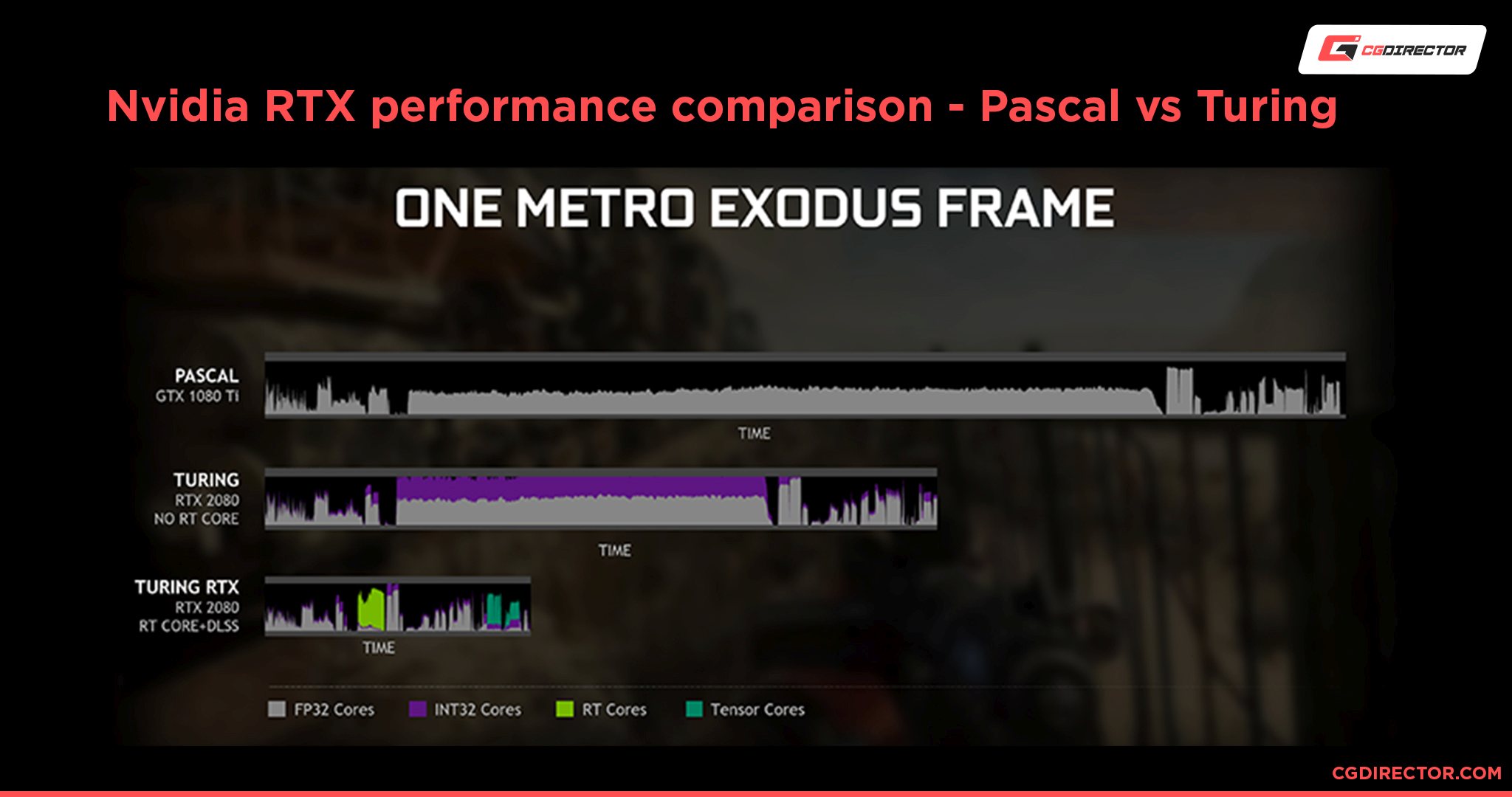
Both in Benchmarks by Nvidia (Image above) and according to benchmarks carried out by PC Gamer – when testing the equivalently priced GeForce RTX 3080 with the Radeon RX 6800 XT – Nvidia’s Ampere architecture displayed almost twice the ray tracing frame rate performance of its competitor.
Requirements for Using RTX & Ray Tracing
For rendering stills or videos, enhanced by ray tracing, any GPU can be used. But in order to enable ray tracing for real-time applications, you will need the appropriate hardware components and applications.
Hardware
When it comes to graphical processors that include hardware components (or processes) dedicated to ray tracing, there is only a short list of compatible GPUs.
This includes:
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 20 Series
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 30 Series
- Nvidia Quadro RTX
- AMD Radeon RX 6000 Series
Important to mention is that gaming consoles – particularly the Playstation 5 and Xbox Series X (and S) – do support ray tracing for certain gaming titles.
Software Support
If you have a previous-generation GPU that does not include dedicated hardware support, like Nvidia GeForce GTX or AMD Vega and Polaris for example, you can still utilize ray tracing; albeit to a significantly lesser extent.
Nvidia GTX GPUs (1060 and above) can support basic DirectX Raytracing (DXR), made possible via a driver released in mid-2019 by Nvidia.
Also, some game engines, like Unity, provide ray tracing support for Nvidia Pascal GPUs.
Older AMD GPUs do not support ray tracing in an official capacity, but work is currently being done using a Radeon Vulkan driver (RADV) to allow pre-RDNA2 graphics cards to utilize real-time ray tracing.
What Software Makes Use of RTX Features (Ray Tracing Cores) On Nvidia GPUs?
If you have an Nvidia RTX Turing or Ampere GPU, you can take advantage of the RT cores of your graphics card to accelerate rendering tasks or interact with models and scenes using ray-traced lighting in real-time.
Nvidia-Developed RTX GPU-Rendering Solutions
Nvidia offers various in-house tools – for automating, or accelerating, ray tracing tasks – that are compatible with RTX GPUs.

OptiX
Firstly, the OptiX ray-tracing engine is free for commercial use and provides GPU-accelerated ray tracing via an RTX GPU’s inherent RT cores. It also includes an AI-accelerated denoiser as a post-processing feature.
Iray
Using OptiX, Nvidia’s Material Definition Language (MDL), and your GPU’s inherent RT cores, Iray can generate incredibly photorealistic images.
Iray – as a plugin for 3D Software – can also improve 3D and VR rendering workflows, with lighting features like Emissive Geometry, Light Path Expressions, and Photometric Lights.
Iray can be incorporated into existing 3D content creation applications, or via SDK integration.
Omniverse
For workflows that integrate photorealistic ray-traced rendering, the Omniverse platform allows for real-time virtual collaboration in a shared virtual space.
Though currently in open-beta form, Omniverse has a wide list of connectors, ranging from Autodesk 3DS Max to Adobe Photoshop.
RTX-Technology Enabled Workstation Applications
Artists and content creators alike can find a list of over 40 3D rendering applications and plugins that make use of Nvidia’s RTX ray tracing technology and AI creative tools.
A few examples of compatible engines are Blender’s Cycles, Octane, Redshift, DaVinci Resolve, Unreal Engine, Unity, NX RT studio, and Adobe Dimension.

If you’re looking to build a high-end workstation PC for 3D modeling and rendering, the following article has both a generalized guide, as well as a list of components that are best for these workloads.
Gaming Applications
Though not all games take advantage of ray tracing technology, there is a respectable list of popular titles that have implemented this feature. Such games include Cyberpunk 2077, Quake II, STALKER 2, Fortnite, and Resident Evil Village; to name a few.
How to Enable RTX
If you meet the aforementioned hardware conditions, and the application you wish to use supports ray tracing, then you can enable the process directly from the application.
Other than the installation of the latest GPU driver (Nvidia, AMD), and Microsoft DirectX 12 API, no further step needs to be taken from your desktop.
For games specifically, the graphical setting you want to look for – in the in-game menu – will either be referred to as “Ray Tracing”, “DXR”, or “RTX”.
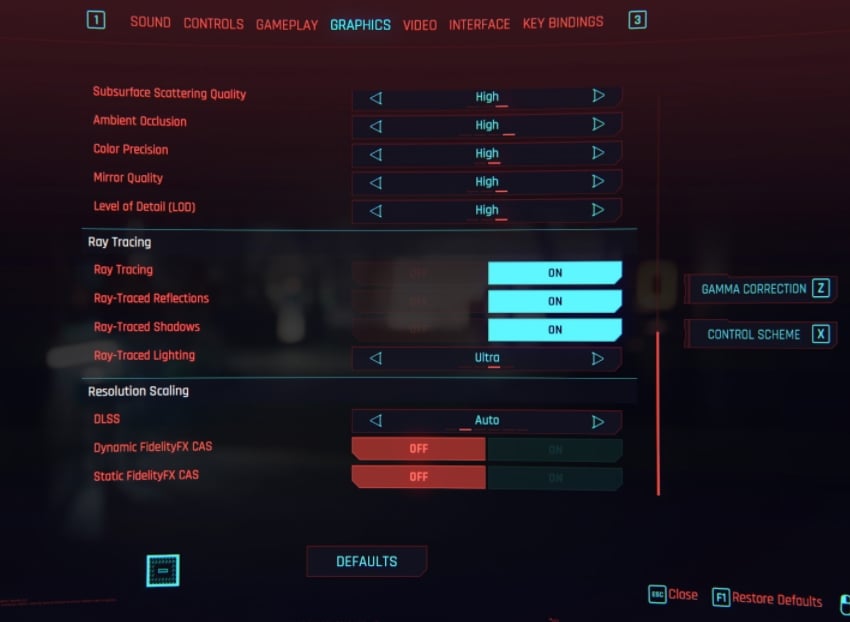
In-Game Setting for enabling RTX in Cyberpunk 2077
If you cannot find this setting, then either the game itself does not support Ray Tracing, or you are not using DirectX 12 or DX 12 Ultimate. For Steam users, make sure to check that the game is using the proper version of DirectX on launch.
Professional Applications, such as GPU Render Engines will each have their own setting that you might have to enable within your 3D Modeling Software prior to rendering.
Here’s what this looks like in Cinema 4D and the GPU Renderer Octane:
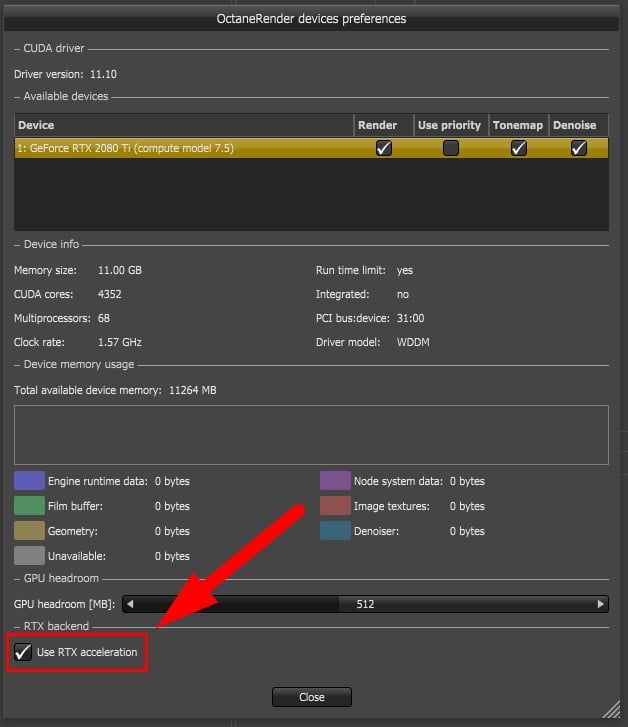
What Is RTX Voice and How to Enable It on Your Nvidia Graphics Card
Now that we’ve gone through ray tracing, and how it relates to Nvidia’s RTX technology, let’s take a look at the AI-powered RTX Voice application.
What Is RTX Voice and Is It a Big Deal?
RTX Voice works to eliminate background noise from your voice communications in real-time. This can be incredibly useful for anything from streaming, to video conference calls.
What makes RTX Voice even more worthwhile, is the fact that it filters both your background noise, as well as the incoming noise emissions from others on the call.
In other words, your friends or colleagues can hear your voice clearly, and you can hear their voice devoid of any excessive ambient sound pollution.
RTX Voice works on a host of supported applications; of which you can find a comprehensive list here.
Can You Use RTX Voice on GTX GPUs?
RTX Voice really has nothing to do with the RTX nomenclature and its encompassing architecture.
Ray tracing is not utilized for this application, and though Nvidia initially mentioned that this technology was made possible with Tensor Cores, they later retracted this assertion.
The reason for this abjuration may be related to a hack that was created, making RTX Voice compatible with GTX GPUs.
Soon after that, Nvidia allowed RTX Voice to officially be compatible with Nvidia GTX graphics cards that have a 410.18 (or newer) driver.
How to Enable RTX Voice
Currently, you can either download RTX Voice as a standalone application, or integrated in Nvidia’s Broadcast application.
Note that Broadcast is only available for Nvidia GeForce RTX 2060, Quadro RTX 3000, Titan RTX or higher GPUs; and it requires Windows 10 64-bit.
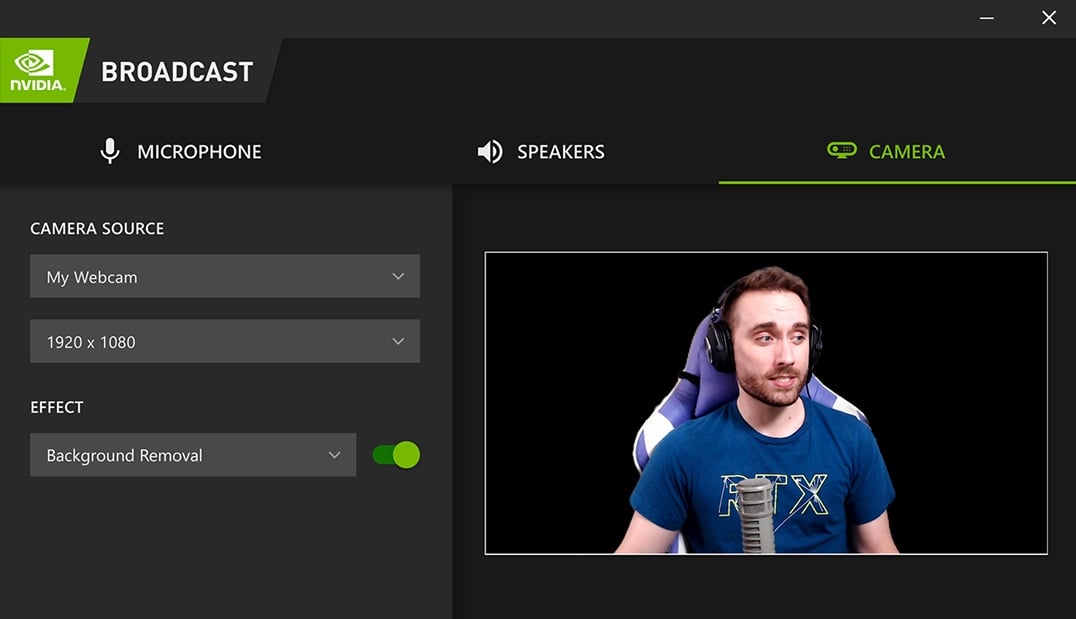
If you wish to download RTX Voice, the setup process is fairly simple. Download the application, install it, and enable background noise removal.
For instructions on how to arrange RTX Voice for specific compatible applications, make sure to check Nvidia’s official guidelines.
When to use RTX Voice
Though RTX Voice is incredibly useful for applications that deal with real-time voice communication, it may become a hindrance for pre-taped voice recordings.
When RTX Voice filters noise, there are minor blemishes and artifacts that are introduced to the audio; and may overlap with the dialogue.
These defects are easily ignored when heard in real-time, but they can be distracting and unpleasant when editing audio. The resulting distortions are also difficult – if not impossible – to remove.
For pre-recorded audio, it is best to use an application – like Adobe Audition or iZotope RX 8 – to clean and restore the audio in the post-production process.
Conclusion
As technology advances, computer-generated photorealistic images & videos are transitioning from pre-rendered commodities to real-time experiences.
Real-time ray tracing is still in its infancy, as techniques like photon mapping and path tracing are still being implemented.
Now is the time to invest in taking full advantage of what real-time ray tracing has to offer.
From the perspective of a content creator, or simply as a means of indulgence through gaming, enabling and making use of your GPU’s RTX capabilities is a must.
Over to you
How do you plan on using your GPU’s ray tracing potential? Do you have a favorite gaming title or render engine that is RTX compatible? Let us know in the comments below.
Also, if you need additional help setting up your ray tracing application, make sure to visit our expert forum!

![Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step] Guide to Undervolting your GPU [Step by Step]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/04/Guide-to-Undervolting-your-GPU-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

![Are Intel ARC GPUs Any Good? [2024 Update] Are Intel ARC GPUs Any Good? [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/02/Are-Intel-ARC-GPUs-Any-Good-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Graphics Card (GPU) Not Detected [How to Fix] Graphics Card (GPU) Not Detected [How to Fix]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/01/Graphics-Card-GPU-Not-Detected-CGDIRECTOR-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments