TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is a motherboard’s chipset and what makes it so important?
Why should you, the end user, care about something as granular as a motherboard’s chipset when components like thousand-dollar graphics cards exist?
Let’s dive in and find out!
What is a Motherboard’s Chipset?
If you were to compare the anatomy of a PC to the anatomy of a human, the motherboard is essentially the “spine” of the PC to which everything else is connected.
It’s just as important as big-name components like the CPU (Central Processing Unit) or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), even if it doesn’t have a visible performance impact.
And one of the more impactful components of a motherboard will actually be that motherboard’s chipset, which controls the communication between everything that’s attached to it.
Here’s how Intel defines a motherboard’s chipset:
The chipset is a silicon backbone integrated into the motherboard that works with specific CPU generations. It relays communications between the CPU and the many connected storage and expansion devices.
Below’s a graph of a modern Intel motherboard with a Z790 chipset and a 13th Gen Intel Core CPU.
If you look at all the components (in blue), you’ll notice a couple of things straightaway:
- A few components like RAM, some PCIe slots, and a high-speed storage slot or two, can communicate directly with the CPU.
- The vast majority of connected devices need to go via the chipset to communicate with the CPU (using that single DMI link). Just look at how much is connected to the chipset (bottom)!
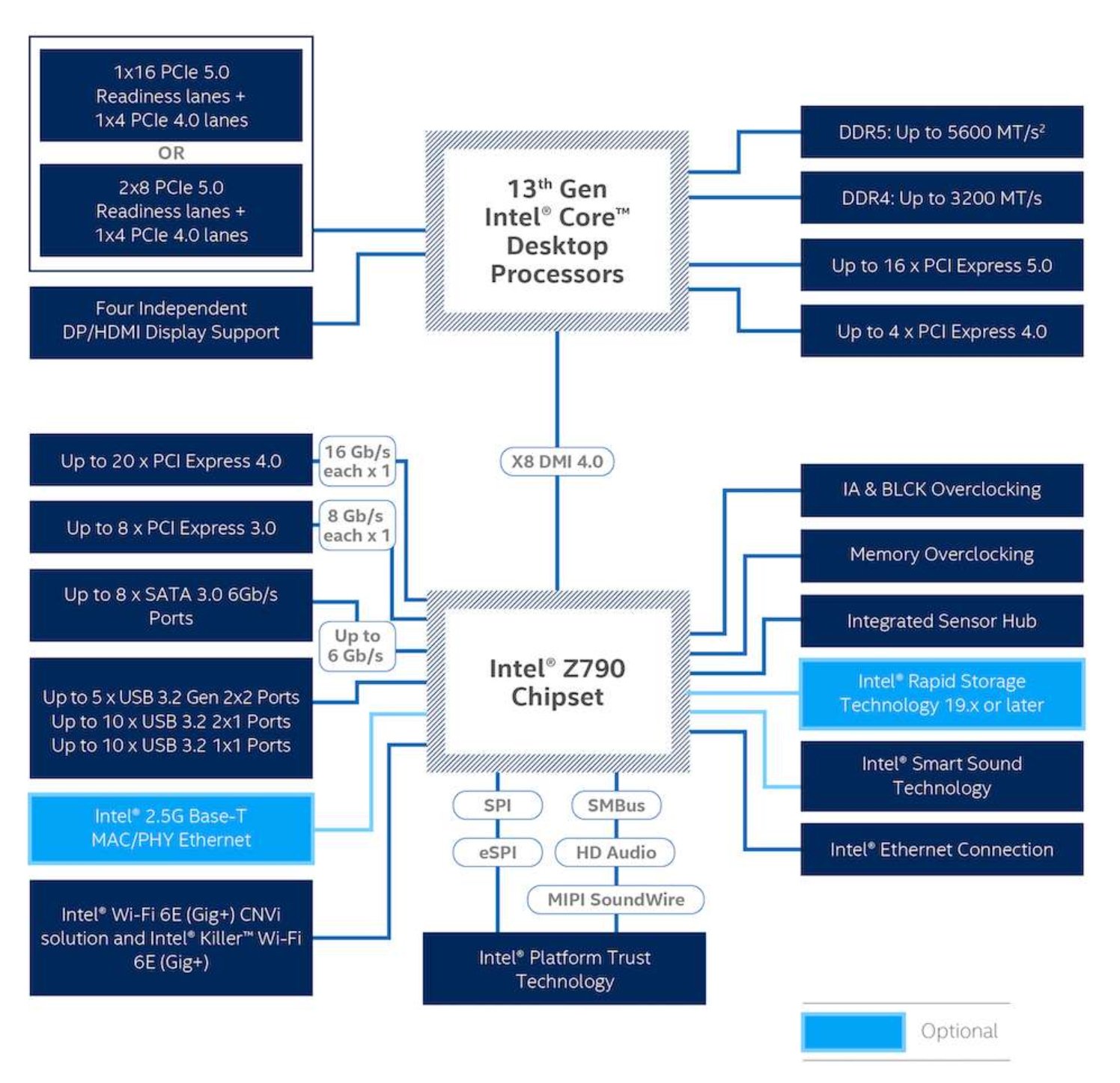
Image Source: Intel
In addition to letting your CPU communicate with a multitude of components, a motherboard chipset also often dictates compatible CPUs. In fact, the motherboard’s chipset is the true determiner of out-of-box processor compatibility, as CPU sockets can be reused for future releases.
Of course, BIOS updates can also add CPU compatibility after-the-fact. But a BIOS update cannot add functionality to a cheap chipset that bring it anywhere close to the capabilities of a high-end chipset.
How does a Motherboard’s Chipset impact PC features?
While a motherboard’s chipset handles a lot of things, you can generally break down Chipset differences into the following four categories: Overclockability, RAM Capacity, RAM Speed, and PCI Express + I/O Support.
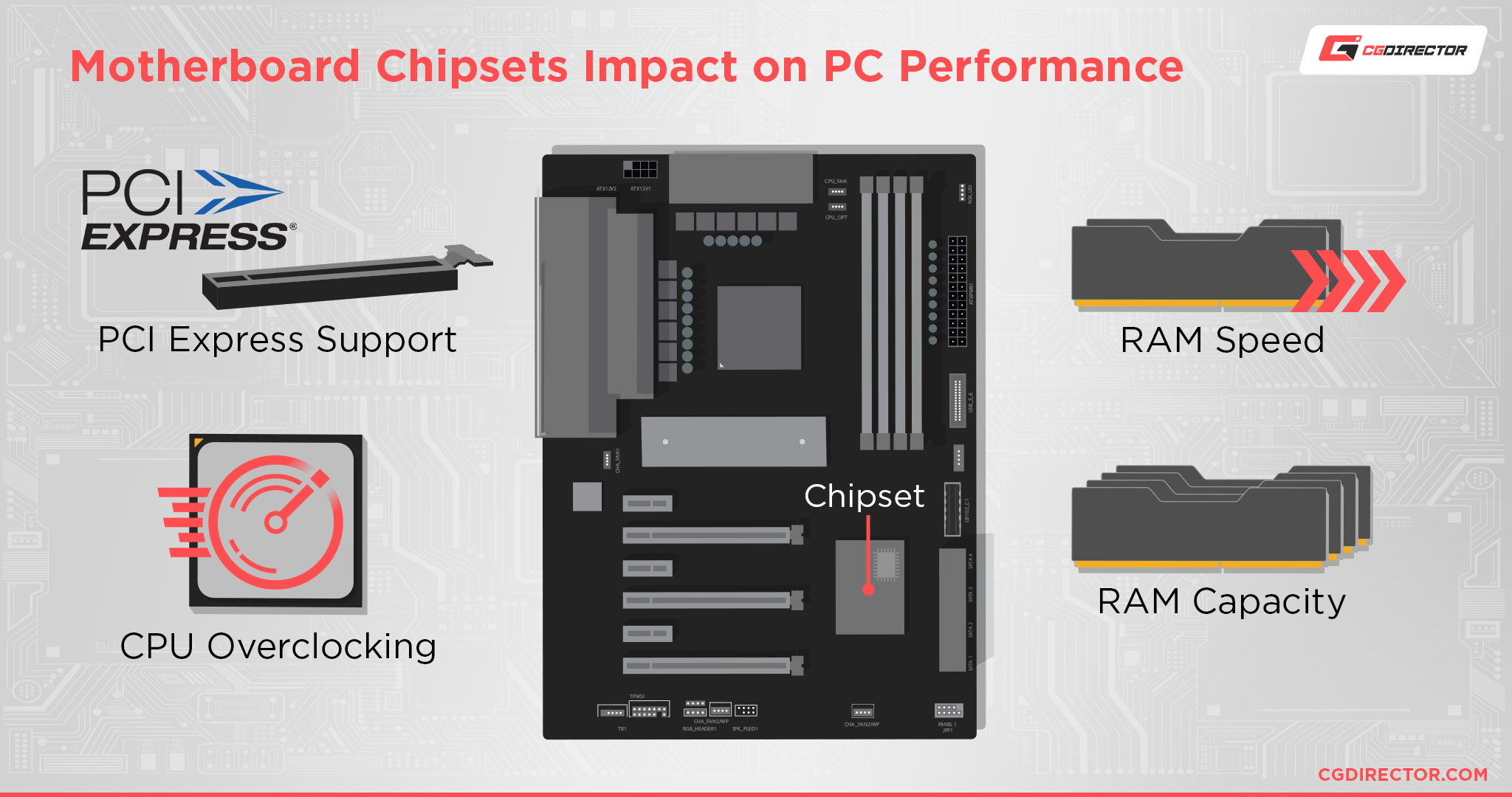
Here’s an overview of how different modern Intel chipsets compare:
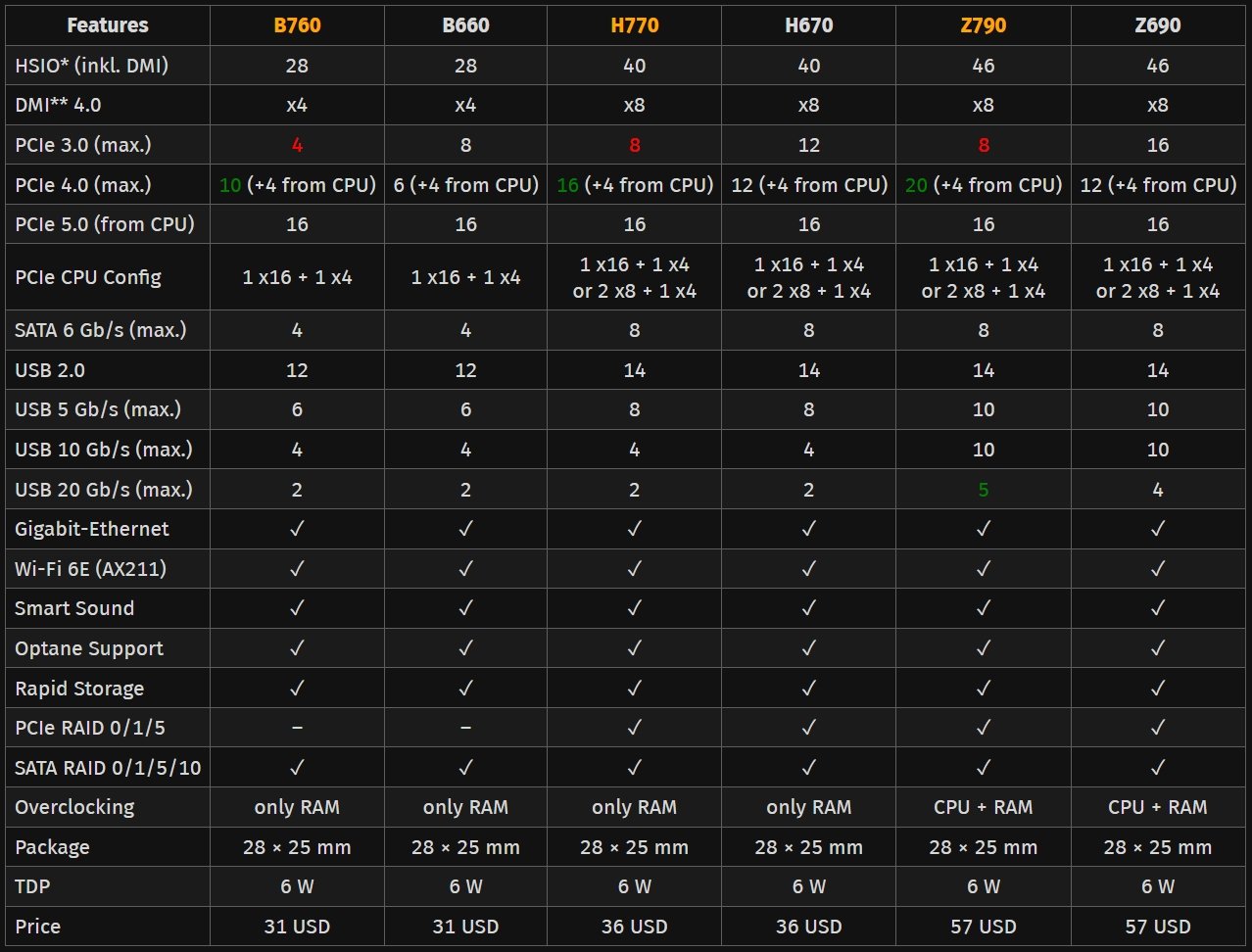
As you can see, they can differ considerably in things like the amount of PCIe Lanes, USB, DMI (which dictates how fast the chipset can communicate with the CPU, very important!), and overclockability, or RAID capability.
Each generation of motherboards though will have its own new and shiny tiers of chipsets, so be sure to dig into the specifics for the generation you’re looking to buy.
CPU Overclocking
Depending on your motherboard’s chipset, your motherboard may or may not offer support for CPU overclocking.
CPU overclocking, especially with the right cooling setup, is a way to manually increase your processor’s performance. However, access to this feature is often restricted by Chipset (especially on Intel).
Other factors tie into CPU overclockability on the motherboard besides just the Chipset, though. For example, a motherboard’s VRMs, and the general quality of the electronics built into it, have a high impact on a CPU’s OC potential and stability.
The VRM, or the Voltage Regulator Module, is vital for controlling and “cleaning” power to the CPU in all scenarios, which means higher quality VRMs are generally better suited for overclocking.
That said, even though chipset tier doesn’t really determine quality of components, manufacturers will generally use better materials and electrical components on products featuring top-tier chipsets (for example, Z790 on the Intel side and X670 on the AMD side).
Memory Overclocking Support
Setting a memory clock higher than the current JEDEC standard (for example, DDR4-3200 for DDR4 memory) is basically memory overclocking. Any kits on shelves with speeds higher than this JEDEC spec require an “overclock” to get there.
However, manufacturers often limit memory overclocking support on budget chipsets. In fact, until very recently, Intel disabled memory overclocks even on its mainstream B-series chipsets – forcing users to opt for a Z-series board instead.
PCI Express & I/O Support
Last but not least, the chipset also defines the maximum number of PCI Express lanes available to your motherboard manufacturer. How they choose to allocate these lanes, is dependent on the manufacturer, though.

Even though the slot has a mechanical length of a x16 slot, the pins only reach up to x8 length.
There’s a lot of nuance to breaking down the difference between PCI Express Lanes and PCI Express Slots, but a chipset with more Lanes is better, especially if you’re using multiple high-speed GPUs or NVMe drives.
How PCIe Lanes are used and provided by the chipset will also determine what kind of I/O your PC can use, whether its additional USB ports, multiple LAN ports, 10G LAN, Thunderbolt, you name it. All of this is routed and managed through the motherboard’s chipset.
How does a Motherboard’s Chipset impact PC performance?
How can you actually expect a motherboard chipset to impact your PC’s performance?
Well, the chipset by itself isn’t going to have very much performance impact on its own, but the features granted to your PC by your chipset (CPU overclocking, added PCIe-Lanes through the chipset, etc.) can have a huge performance impact.
Don’t expect the motherboard chipset by itself to really have an impact on your PC’s performance.
The PCI Express Lanes, overclocking capabilities, and limits applied to your chipset will apply to the rest of your PC, though!
Always make sure that you’re buying a motherboard with a chipset actually suited to what you’ll be doing with your system.
If you aren’t going to be overclocking or running high-end storage devices at all, for example, going with entry-level motherboards featuring cheaper chipsets can save you some money.
If your system is geared towards high-end productivity and you want to run multiple GPUs, use several high-speed USB connectors, or want something like RAID capability, your choice of motherboard and chipset should reflect that.
On the Intel side of things, only their highest-end chipset even supports CPU overclocking, which helps streamline your choices. With AMD, most of their chipsets support CPU overclocking immediately, but you’ll still gain access to things like more I/O and premium features on the top-tier X-series chipsets.
How else does a Motherboard impact PC performance?
Well, that was most of it!
A motherboard’s assigned chipset will tell you most of what you need to know about how your performance will be impacted, but it does not necessarily tell the entire story.
The rest of your motherboard’s specifications are fairly important, too, but largely speak for themselves- so what else could I be talking about?
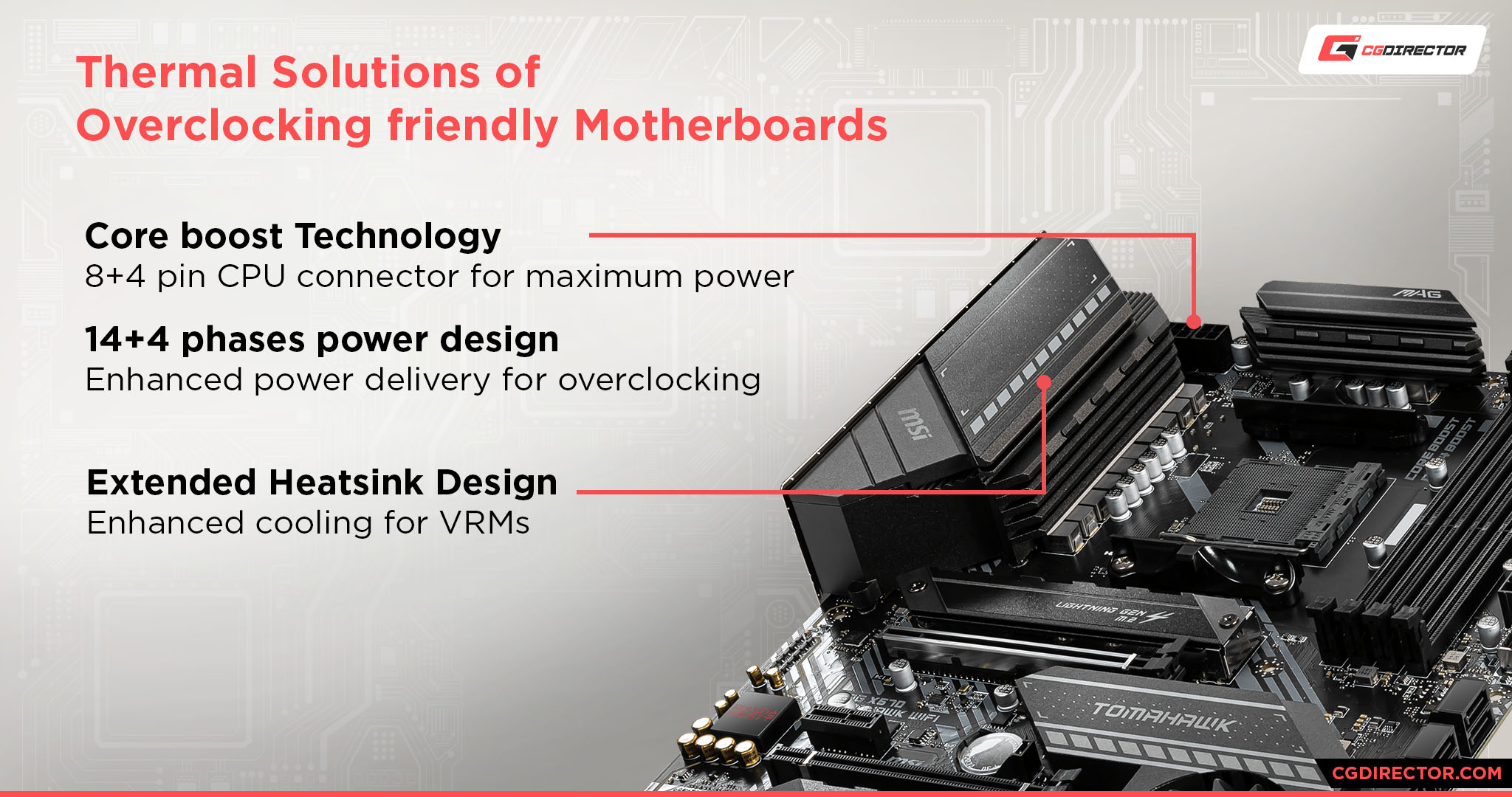
VRMs and build quality, baby! A motherboard’s VRM, or Voltage Regulator Module, is composed of multiple “Phases”.
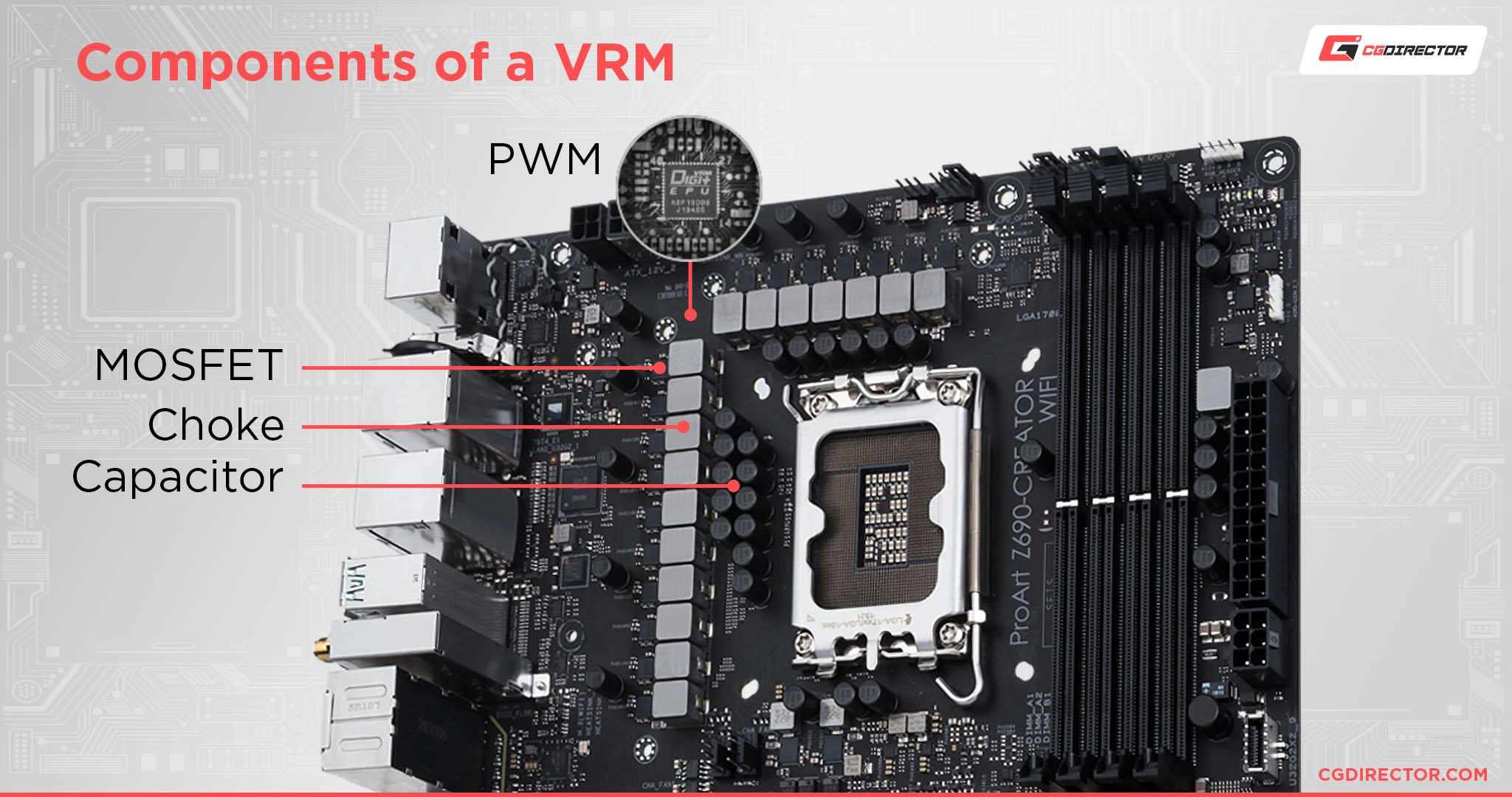
The quality of your motherboard’s VRM will determine the stability and quality of its power delivery to your CPU, which is one of the most important components in your whole system.
If you’re looking to overclock or are using a high-end CPU with high Boost clocks, it’s very important to make sure that your motherboard’s VRM is up to the task.
FAQ
What are Motherboards Made Of?
Mainly fiberglass and copper, if we’re being reductive and referring only to raw materials. There are many more components of a motherboard to speak of, though.

Image Credit: ASRock
Throughout this article, we’ve been focused on just one component of the motherboard: the chipset.
Like most components of a motherboard, the chipset has an important and irreplaceable job that needs to be done for the whole system to function, even if the end-user isn’t aware of that chipset at all.
Interested in learning a little more about what other components motherboards are made of and how motherboards are assembled? Peruse the extended guide, especially if you’re trying to narrow down all the nameable components of your PC.
How much do Motherboards cost?
The answer to this question very much depends on the motherboard, as motherboards can start fairly cheap ($60 or under), but high-end and enthusiast boards climb into the hundreds and, on rare occasions, thousand(s) of dollars.
Fortunately for you, the inquisitive reader, I’ve already written an extended guide on how much motherboards cost and what makes the motherboard pricing tiers different. Consider that guide if you want to know more about the “pricing” side of things.
What does ATX stand for in Motherboards?
ATX stands for “Advanced Technology eXtended”, and refers to the “standard” form factor used by most PC motherboards and cases.
An ATX motherboard will require a case with support for ATX or larger Extended ATX boards in order to be installed, for example.
For more on the ATX form factor, related form factors, and how these things impact motherboards, consider the extended guide!
Over to You
And that’s it! I hope this article helped teach you a thing or two about motherboard chipsets and how important they can actually be when picking out your PC build.
I tried to write this article to be as “Evergreen” as possible, so I don’t have any specific board or chipset recommendations, but feel free to ask for help with these things in the comments section below! Me or another member of the CGDirector Team will be happy to help you out.
Alternatively in the comments section, you can also sign up for the CGDirector Forums. Our expert team and enthusiast community is plenty active, and the forums should be a good place to get feedback or tips on your current PC project.
Until then or until next time, have a good one! And remember: if you wanna overclock, make sure your chipset supports it…and that your VRM is up for the task.
![Where Do You Connect PC Fan PWM Cables To? [Beginner’s Guide] Where Do You Connect PC Fan PWM Cables To? [Beginner’s Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/12/Where-Do-PWM-Cables-Go-Beginners-Guide-Twitter-1-594x335.jpg)
![How To Connect Front Panel Cables To Your Motherboard [Guide] How To Connect Front Panel Cables To Your Motherboard [Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/01/How-To-Connect-Front-Panel-Cables-To-Your-Motherboard-Twitter-copy-1-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments