TABLE OF CONTENTS
If your motherboard has more than one PCI Express slot, it may not be immediately clear which one is going to be the best for your graphics card to use.
I’m going to use this article to clear up this and related questions, including:
The Basics of PCI Express
PCI Express is the de facto expansion card connector standard for modern motherboards and is known for offering fairly high bandwidth and speeds.
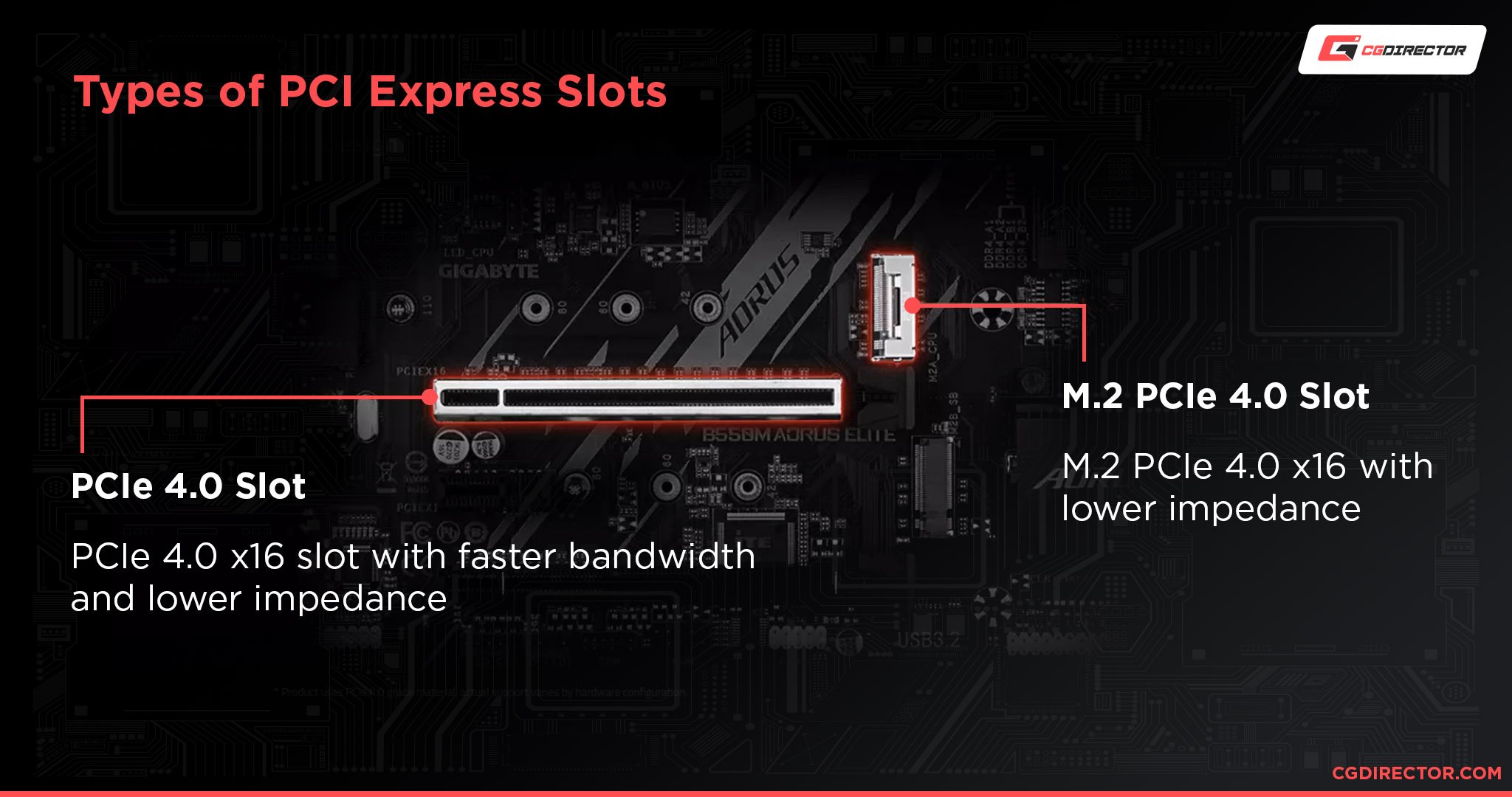
PCIe Slots come in a few variations, but they all allow high-speed connection to your chipset and your CPU through so-called PCIe-Lanes that are tiny physical wires which run throughout your motherboard.
Types of expansion with PCI Express include graphics cards, capture cards, sound cards, SSDs, and more.
If it can expand the functionality of your PC and you can’t just plug it in via a USB cable, chances are high that you’ll be looking at a PCI Express expansion instead.
Like other standards, PCI Express is a standard that has evolved over time to include generations of tiered performance.
These tiers include the following:
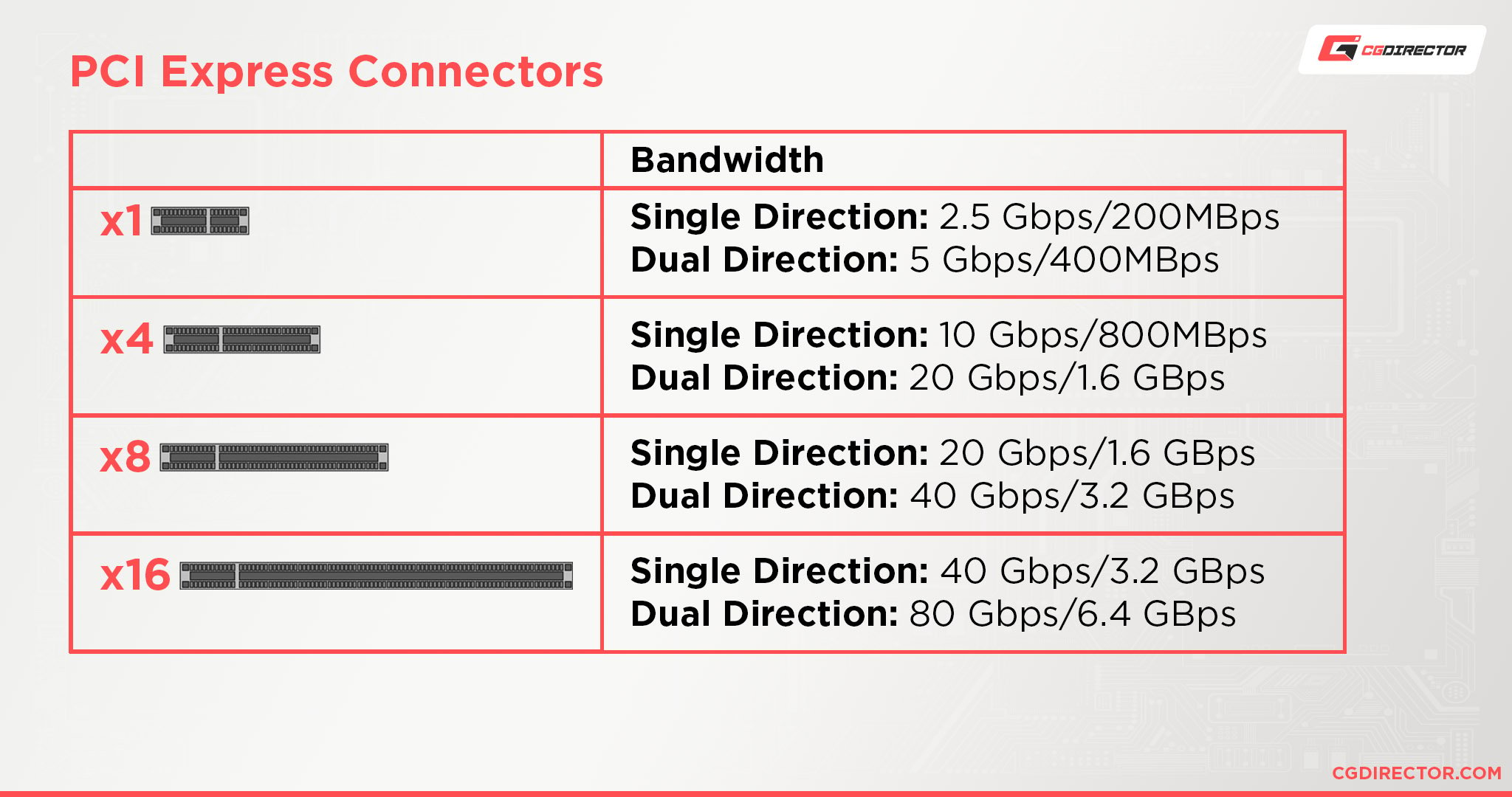
| PCIe Bandwith | Transfer Rate | Bandwidth x1 (per lane) | x4 | x8 | x16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe 1.0 | 2.5GT/s | 250 MB/s | 1.00 GB/s | 2.00 GB/s | 4.00 GB/s |
| PCIe 2.0 | 5GT/s | 500 MB/s | 2.00 GB/s | 4.00 GB/s | 8.00 GB/s |
| PCIe 3.0 | 8GT/s | 984.6 MB/s | 3.94 GB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s |
| PCIe 4.0 | 16GT/s | 1969 MB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s | 31.51 GB/s |
Generally, graphics cards benefit from running at the higher speeds (read: bandwidths) offered by PCI Express, usually by running with x8 or x16 PCIe lanes.
PCIe Lanes – or Why Slot Choice Matters
So, now you have a basic understanding of what PCI Express is and what bandwidths it can achieve. How does this impact which PCIe slot to choose for your graphics card?
Well, depending on the PCIe slot you choose, your graphics card may function differently.
Especially when you’re using high-end graphics cards, making sure that your PCIe slot has access to 8-16 PCI Express lanes is important.
If you attempt to run your graphics card without enough PCI Express lanes, you’ll experience reduced performance.
The number of PCIe Lanes directly relates to the bandwidth your expansion card or graphics card will have access to. Simple add-in cards such as Sound-Cards don’t need many PCIe Lanes (x1 or x4) but GPUs send and receive so much Data over the PCIe-Bus, that most require 8-16 to run without throttling.
Finding Which PCIe Slot For Your Graphics Card Is Best
So, which PCIe slot is best for your graphics card?
In general, the first PCI Express slot on your motherboard will be the best one to install your graphics card into.
The first slot will usually be a fully-decked PCIe x16 slot that will allow your graphics card to run at its full performance, and it may be one of the only x16 slots available on the motherboard.
PCIe Slots vs PCIe Lanes
In order to understand the following few paragraphs, we have to make sure the difference between PCIe-Slots and Lanes is apparent.
In the image above you can see PCIe-Slots that have different lengths. The longest is defined as “x16”, then x8, x4, and the shortest is x1.
This designates physical properties (mostly length) of mechanical PCIe-Slots and doesn’t necessarily tell us too much about the potential bandwidth of these slots yet.
So far so good.
Electrical PCIe-Lanes, though, are physical wires that run from those Slots to the motherboard and throughout the motherboard, either to the CPU or Chipset. PCIe-Lanes designate the transfer bandwidth a PCIe-Slot is capable of.
Unfortunately, PCIe-Lanes, too, are named in the same way as Slots and often used interchangeably (even though they shouldn’t be used interchangeably). x16, x8, x4, x1.
To confuse things further, these don’t always correspond to each other. It would make sense to think a x16 PCIe-Slot will have x16 PCIe-Lanes, and that’s that.
Depending on the factors we discuss below, though, a mechanical x16 Slot could run at just x8 or even x4 PCIe-Lanes.
So even though your Graphics Card fits nicely into a mechanical x16 PCIe-Slot, this doesn’t mean that Slot will run at x16 PCIe-Lanes.
Let’s take a closer look at why this is so:
Which PCIe Slots To Use For Multi-GPU Setups
What if you’re using more than one graphics card?
Well, the installation of your first graphics card should still go to your first open PCI Express x16 slot.
From here, any subsequent GPUs will need to be mounted in the available PCI Express slots below, specifically, ones that offer at least 8 PCI Express lanes.
This is where things can get tricky.
Even though the first PCIe-Slot (the one closest to your CPU) is usually guaranteed to run at x16, there’s more to it than that.
A Motherboard’s Chipset and the type of CPU you are using dictates the amount of available total PCIe Lanes. These Lanes will be split differently, depending on how many components you have installed in your system.
If you have a lot of SATA Devices or M.2 NVMe SSDs, it might very well be that PCIe Lanes are already used up and you will not be able to add another GPU.
Mainstream Chipsets (such as X570, B690, B660) also divide their lanes between the amount of GPUs you have installed, so one GPU would use x16 Lanes, but if you install 2 GPUs, they will both be able to use only 8 Lanes each.
Long story short: Especially for multi GPU setups, consult your Motherboard Manual and look for a VGA / PCIe Bandwidth (sometimes named differently) overview table like this one on the MSI Unify x570 Motherboard:
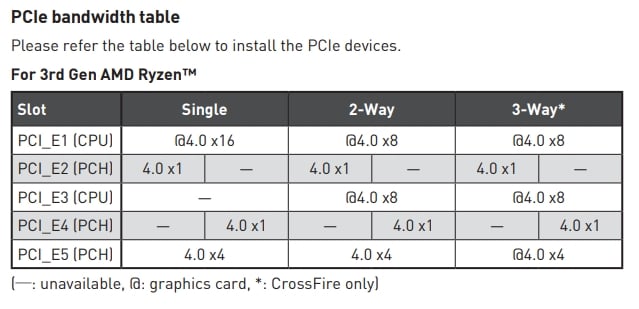
MSI Unify X570 PCIe Bandwidth Table
The table above shows how, on the MSI Unify X570, you can have a single GPU at x16 PCIe-Lanes, but two GPUs will then run at x8 PCIe-Lanes. With 3 GPUs, two will run at x8, one at only x4 – this will severely throttle the third GPU in many workloads.
Our guide to setting up multi GPU configurations for GPU rendering takes an in-depth look at this topic.
Where You Shouldn’t Install Your Graphics Card
So, if you’re supposed to prioritize using the first available PCI Express x16 slot, what happens if you install it somewhere else?
Well, it depends on the slot. If you install your graphics card in a PCI Express x8 slot instead of an x16 slot, you should experience only minimal performance loss when compared to using an x16 slot.

However, graphics cards become particularly crippled by the use of weaker slots than that, especially x4 slots.
You may still be able to get away with using a PCI Express x4 slot with new motherboards and lower-end graphics cards, but this still isn’t recommended.
Some PCIe Slots are hooked up to the Motherboard’s chipset instead of to the CPU. This can severely impact your Graphic Card’s performance as well. The GPU performs best if it can exchange data through PCIe-Lanes directly with the CPU, without the need of routing through your Chipset.
Routing through the Chipset involves the DMA (Direct Memory Acces which is the connector between Chipset and CPU), which will become a bottleneck and also throttle any other components (such as storage) that are hooked up to the chipset.
Stick with your fastest x8 and x16 slots that have direct CPU PCIe-Lanes for the best results! Your Motherboard Manual will tell you which slot this is.
FAQ
How Many PCIe Lanes Do I Need?
For graphics cards, you’ll always get the best results by using the fastest available PCI Express x16 slot.
PCI Express x8 slots can be acceptable when doing a multi-GPU setup as well, but even then motherboards that support multiple x16 slots can be a better choice for multi-GPU builds.
Outside of graphics cards, PCI Express lanes can also be put to work by other forms of expansion, including SSD storage.

ORICO M.2 NVME to PCIe 3.0 X4 Expansion Card
Fortunately, you typically only need PCIe x4 slots for the majority of expansion cards, with x16 and x8 being generally reserved for graphics cards.
To learn more detailed information about how many PCIe Lanes You Need, especially per workload, try out Alex’s PCIe Lanes Guide.
What About Mini ITX and Micro ATX Motherboards?
When it comes to Mini ITX motherboards, you don’t really need to worry about which PCI Express slot to use, as there should only be one x16 slot available.
However, because there is only one slot, you also won’t be able to do a multi-GPU setup with a Mini ITX motherboard.
With Micro ATX motherboards, the wisdom of picking the first available x16/x8 slot for your graphics card still applies.
Multi-GPU may or may not be possible depending on the availability and layout of other PCI Express slots on a Micro ATX motherboard.
Some boards will opt to have extra M.2 slots in the place of open PCI Express slots on the motherboard.
Where Do I Install My GPU’s PCIe Riser?
If you’re using a PCI Express Riser or extension cable inside your build, be sure to follow the same rules laid out above and prioritize using x16 or x8 slots for your graphics card.

The last thing you want is to plug your Riser into a speed-restricted slot and end up losing precious graphics performance.
Do Laptops Have PCI Express Slots?
Generally-speaking, no, but that doesn’t mean that you can’t add expansion to a laptop.
In fact, some laptops even allow you to add an external GPU upgrade!
If you’re looking to add a GPU or an SSD upgrade to your modern laptop, you’ll want to look for a laptop that supports Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4, or another high-end connection standard.
With supported devices, you can use a Thunderbolt cable routing to an external dock holding a full desktop graphics card that can be utilized by your laptop.
This is a great way to get extra power out of your laptop if it supports Thunderbolt, and can blur the lines between laptop and desktop.
Over to You
And that’s it, for now! I hope that this article helped teach you which PCIe slot to use for your graphics card and why. If you have any lingering questions or other concerns, feel free to ask us in the comments or our forum!


![What Does PCIe x16 Mean? [Beginner’s Guide] What Does PCIe x16 Mean? [Beginner’s Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2022/11/What-Does-PCIe-x16-Mean-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

2 Comments
12 February, 2024
Thanks. Gen 3 pcie slots, 4070 Super upgrade? maybe not..
18 October, 2022
Awesome article! Thank you, I’ve found everything what I need.